FR4 laminate with UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB
What is classification of UL94?
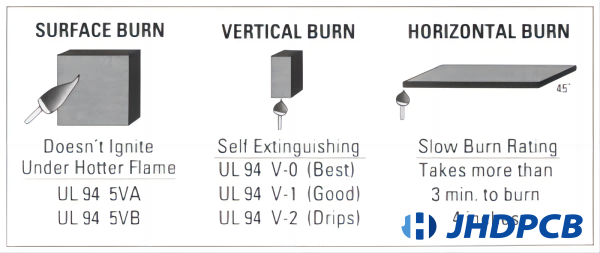
UL 94 is widely recognized as the preeminent flammability standard for plastics in the United States. The standard evaluates the burning characteristics of plastics based on a variety of factors, including their orientation and thickness, and classifies them according to their flame-retardant properties. Specifically, ,flammability ul94 categorizes plastics into six different classifications, ranging from the least flame-retardant (Class HB) to the most flame-retardant (Class V-0). This classification system is used by engineers and manufacturers to select appropriate materials for specific applications, such as electronics or automotive components, where fire safety is a critical concern. The standard provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating plastic materials, including testing protocols, test equipment, and requirements for reporting test results. By adhering to UL 94 standards, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet rigorous safety standards and help prevent fires from occurring in a variety of settings.
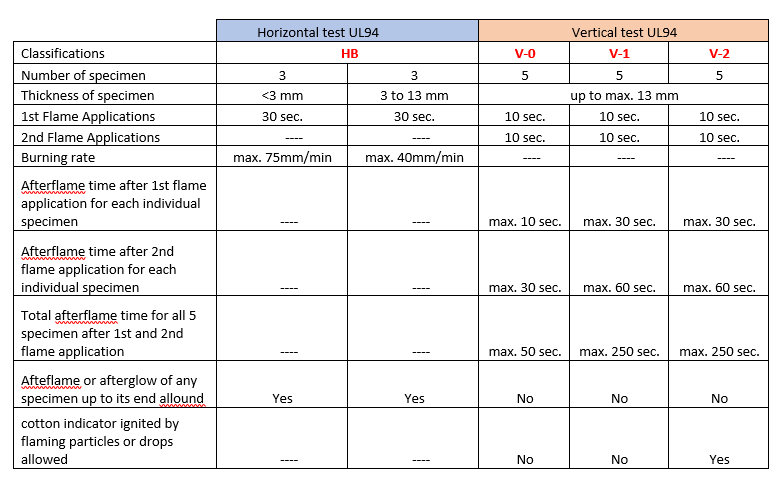
| UL 94 Rating | Definition of Rating |
|---|---|
| HB | Slow combustion on a horizontal specimen; Burning rate is less than 76 mm/min for thickness less than 3 mm or burning stops before reaching 100 mm |
| V-2 | Flames extinguish within 30 seconds after removal of the test flame from a vertical specimen; Dripping of flaming particles is permitted |
| V-1 | Flames extinguish within 30 seconds after removal of the test flame from a vertical specimen; Dripping of particles is allowed if they are not burning Flames extinguish within 30 seconds after removal of the test flame from a vertical specimen; Dripping of particles is allowed if they are not burning |
| V-0 | Flames extinguish within 10 seconds after removal of the test flame from a vertical specimen; Dripping of particles is allowed if they are not burning |
| 5VB | Flames extinguish within 60 seconds after removal of the test flame from a vertical specimen; No dripping is allowed; Specimens may develop a hole |
| 5VA | Flames extinguish within 60 seconds after removal of the test flame from a vertical specimen; No dripping is allowed; Specimens may not develop a hole |
What are the effects of flammability?
The flammability of a material can have various effects, including safety concerns, regulatory compliance, and material selection considerations. Here are some additional points to consider regarding the effects of flammability:
- Safety Concerns: Flammable materials pose a higher risk of fire and can contribute to the spread of flames. This can endanger human life, damage property, and cause environmental harm. Choosing materials with lower flammability properties can help mitigate these risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, especially those involved in electrical and electronics equipment, have strict regulations and standards related to flammability. Compliance with these regulations is important for product safety and market acceptance. The UL94 VB test is one such standard that is widely used for assessing the flammability of materials.
- Material Selection: The flammability characteristics of a material play a significant role in material selection for various applications. Materials possessing superior fire-resistant characteristics are favored in scenarios where fire-proofing is of utmost importance, such as in the domains of edifice fabrication, transportation, and electronic goods designed for everyday use. Understanding the UL ratings and selecting materials that meet the desired UL classification (e.g., V-0, V-1) is important.
- Additives and Colorants: Introducing colorants and additives to a material can potentially affect its flammability properties. As a rule, it is recommended to employ base resins devoid of any additives, given that the majority of additives may lack a UL94 certification. If specific additives are required, it may be necessary to work with a compounder to develop a custom flame-retardant blend that meets the desired flammability standards.
- Part Thickness: The thickness of a part can significantly impact its UL rating. UL ratings are measured at various thicknesses, and a material that may pass the flammability test at a specific thickness may fail at a different thickness. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the intended wall thickness of the part and select a material that maintains the desired UL rating across the specified thickness range.
Here is a table summarizing the effects of flammability based on different thicknesses and ul94 fire ratings:
| Thickness | Flame Rating | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0295 in. | V-2 (UL 94) | Moderate flame resistance; self-extinguishes in 30 sec |
| 0.0591 in. | V-0 (UL 94) | High flame resistance; self-extinguishes in 10 sec |
| 0.0787 in. | 5VB (UL 94) | Stringent flame resistance; passes vertical burning test |
In summary, understanding the effects of flammability is essential for ensuring safety, regulatory compliance, and appropriate material selection. Considering factors such as additives, part thickness, and UL ratings can help in choosing materials with optimal flammability characteristics for specific applications.
What is the difference between an HB and a V0 flame rating?
The UL94 flame ratings, including HB and V-0, categorize the flammability performance of plastic materials used in various applications. These ratings help determine the material’s ability to resist fire and provide an indication of its safety and reliability in specific environments.The main difference between an HB and a V-0 flame rating is the orientation of the specimen during testing and the level of flame retardancy required to achieve the rating.
As mentioned earlier, HB is a horizontal burn rating, which means that the plastic specimen is oriented parallel to the work surface during testing. A flame is introduced and subsequently withdrawn, following which the rate of combustion is assessed. In order to earn an HB rating, the plastic must have a burn rate that does not exceed specified limits. However, an HB rating does not imply self-extinguishing characteristics, meaning that the plastic will continue to burn after the flame source is removed. The majority of plastics, in standard injection molding thicknesses, will satisfy the HB specifications without the use of specific additives.
On the other hand, V-0 is a vertical burn rating, which means that the plastic specimen is oriented perpendicular to the work surface during testing. A flame is applied and then removed according to a specified protocol, and burn times and the presence of flaming drips are used to determine the rating assigned. Plastics with a V-0 rating exhibit the highest level of flame retardancy in the UL 94 standard, with no flaming drips and a low burn time. This rating implies self-extinguishing characteristics, meaning that the plastic will stop burning once the flame source is removed. Certain plastics possess inherent self-extinguishing properties, while others necessitate the incorporation of specific additives to attain a V-0 rating.
In summary, the main differences between an HB and a V-0 flame rating are the specimen orientation during testing and the level of flame retardancy required to achieve the rating. While an HB rating indicates a lower level of flame retardancy and does not imply self-extinguishing characteristics, a V-0 rating indicates a higher level of flame retardancy and implies self-extinguishing characteristics.
Types of UL 94 Testing
To ensure the suitability of plastic materials for their intended applications, samples are subjected to the UL standard testing procedure to determine their flammability properties under controlled laboratory conditions.
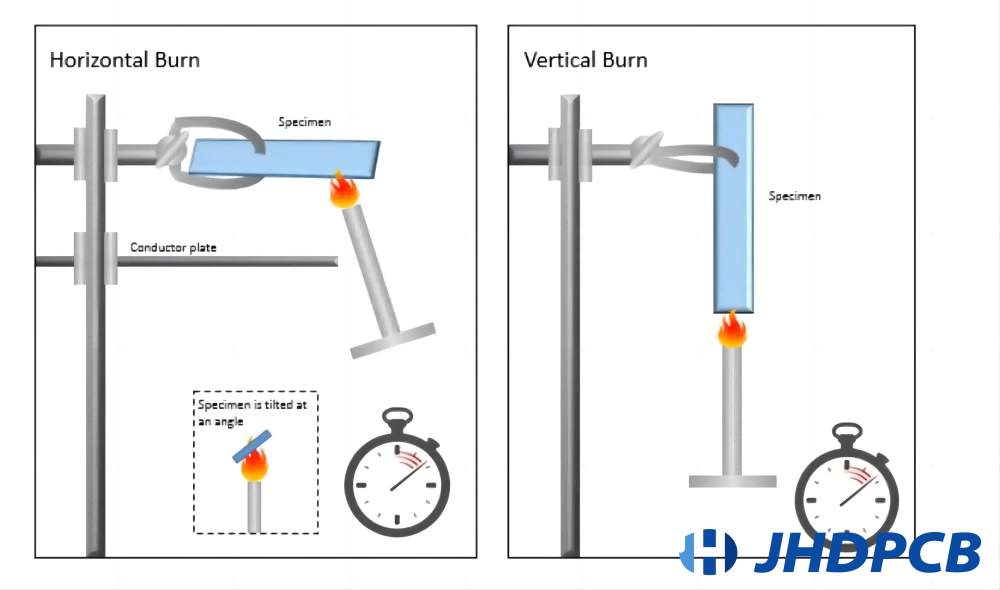
The UL 94 testing involves evaluating the flammability of the material in either a horizontal burn (HB) or vertical burn (VB) position. In these flammability tests, the material is subjected to a flame source for a specified period of time. The test results in one of 12 classifications, with enclosures and insulators falling into the first six classes (5VA, 5VB, V-0, V-1, V-2, HB). The following six classifications are exclusive to low-density foam materials (HF-1, HF-2, HBF) and thin films utilized in electronic circuitry (VTM-0, VTM-1, VTM-2).
Horizontal burning
The HB test evaluates the material’s flammability from a horizontal orientation, assessing whether it burns at a rate below the specified maximum (burning rate less than 76 mm/min for thickness less than 3mm).
Horizontal burning foamed material
In this test, five specimens are exposed to a 38mm flame according to prescribed procedures. After the flame is removed, the afterglow and after-flame times are recorded. A piece of cotton is placed below the specimen to capture flaming particles, and it is noted whether the cotton ignites. The extent of damage to each specimen is also measured. These criteria determine whether the material is classified as 94HF-1 or 94HF-2.
20mm vertical burning test
Five specimens are subjected to a 20mm flame following prescribed procedures. After the flame is removed, the afterglow and after-flame times are recorded. A piece of cotton is placed below the specimen to capture flaming particles, and it is noted whether the cotton ignites. These criteria determine whether the material is classified as 94V-0 or 94V-1.
Thin material vertical burning test
Conducted on solid plastics, this test involves wrapping the specimen around a mandrel. Five specimens are subjected to a 20mm flame according to prescribed procedures. After the flame is removed, the afterglow and after-flame times are recorded. A piece of cotton is placed below the specimen to capture flaming particles, and it is noted whether the cotton ignites. These criteria determine whether the material is classified as 94VTM-0 or 94VTM-1.
After completing the UL 94 testing, the acceptance of the material depends on its conformity to the standards of the equipment or product. The assessment considers various characteristics in end-use applications, such as burn strength, burn intensity, burn rate, ease of ignition, fuel contribution, and combustion products.
What is the standard for test of UL94 HB ?
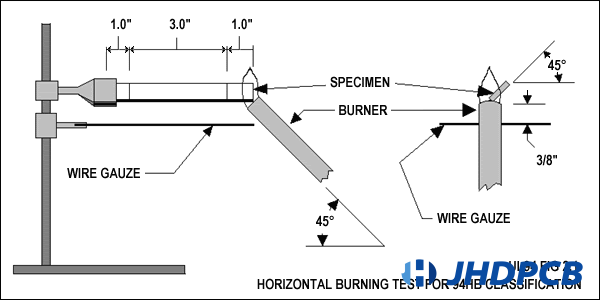
Specimen Preparation:
- Each specimen should be cut to a length of 125 mm (5 in) and a width of 13 mm (0.5 in).
- The thickness of the specimens can vary, typically 1.5 mm (1/16 in), 3.0 mm (1/8 in), or 6.0 mm (1/4 in).
- Before undergoing testing, the specimens necessitate conditioning for 48 hours at a temperature of 23 degrees Celsius and a relative humidity of 50%.
Test Procedure:
- Three specimens of each thickness are used for testing.
- Each specimen is mounted horizontally with its long axis parallel to the surface.
- Additionally, the specimen is inclined at a 45-degree angle with its short axis.
- Two lines are marked on each specimen, one at 25 mm and the other at 100 mm from one end. These lines serve as reference points during testing.
- The specimen is supported at one end, ensuring that its lower edge is positioned 10 mm above a wire gauze.
- A Bunsen burner flame of blue color, with a height of 20 mm, is directed towards the exposed end of the specimen for a period of 30 seconds.
- After the 30-second exposure, the flame is promptly removed.
- If the specimen continues to ignite even after the test flame is removed, the duration for the flame front to propagate between the two gauge marks is recorded.
- This measurement assists in determining the burning rate of the specimen in millimeters per minute.
HB Requirements:
- For specimens with a thickness ranging from 3.0 mm to 13 mm, the burn rate should not exceed 40 mm per minute over a span of 75 mm.
- Alternatively, for specimens with a thickness less than 3.0 mm, the burn rate should not exceed 75 mm per minute over a span of 75 mm.
- In addition to the burn rate, the specimens must cease burning before the flame reaches the 100 mm mark.
It is important to note that these specifications and requirements are used to determine the HB rating, which assesses the horizontal burning characteristics of a plastic material according to the UL94 HB flammability standard. This standard is widely used to measure the plastics flammability and is an essential consideration for materials used in various industries, including electronics, construction, and automotive. The UL94 HB flammability standard ensures that plastic materials used in these industries meet specific safety standards and minimize the risk of fire hazards. Therefore, materials such as FR4, which have high flame retardant properties and meet UL94 HB standards, are extensively used in the manufacturing of electronic devices to ensure safety and prevent fires.
Flame retardant classification of PCB.
PCB flame retardants are classified based on their effectiveness in preventing or slowing down the spread of fire. There are different classifications and standards used to evaluate the flame retardancy of PCBs. Some common classifications include:
1.UL 94:
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) 94 is a widely recognized standard for testing the flammability of plastic materials, including PCBs. It classifies materials into different pcb flame retardant ratings, such as V-0, V-1, V-2, HB, and non-rated.
- V-0: The most flame retardant classification, indicating that the material self-extinguishes within 10 seconds after the ignition source is removed.
- V-1: The material undergoes self-extinguishment within a duration of 30 seconds following the removal of the ignition source.
- V-2: The material self-extinguishes within 30 seconds, but with some burning drips allowed.
- HB: Horizontal Burning, indicating that the material burns slowly in a horizontal position.
- Non-rated: Materials that do not meet any of the above classifications.
2.IPC-4101:
The Institute for Printed Circuits (IPC) defines a range of laminate materials used in the fabrication of PCBs. IPC-4101 specifies different flammability ratings, including FR-4, FR-3, FR-2, and others. FR stands for Flame Retardant.
- FR-4: The most common and widely used laminate material in PCBs, which exhibits good flame retardancy.
- FR-3: A less flame retardant material compared to FR-4, often used in low-cost applications.
- FR-2: A relatively low flame retardant material, used in applications with less stringent fire safety requirements.
3.IPC-CC-830:
This standard focuses on conformal coating materials used to protect PCBs from environmental factors. It classifies conformal coatings based on their flammability, including UL 94 V-0, V-1, and V-2.
These classifications help manufacturers and designers select appropriate materials for PCBs based on the desired level of fire resistance and safety requirements. It is important to consider the specific application and regulations applicable in different industries when choosing flame retardant classifications for PCBs.
What is the importance of UL94 in PCBs?

The UL 94 standard is important because it provides a reliable and standardized method for evaluating the flammability of plastic materials, including those used in PCBs. Here are a few reasons why the UL 94 standard is significant:
- Safety: The primary purpose of the UL 94 standard is to ensure the safety of products and materials by assessing their resistance to fire. By using this standard, manufacturers can determine the flame retardancy of PCBs and select materials that meet specific safety requirements. This aids in minimizing the likelihood of fire occurrences and improves the overall safety of the product.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have regulations and standards in place to ensure the fire safety of their products. Compliance with the UL 94 standard is often a requirement in various sectors, such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Adhering to this standard helps manufacturers demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and ensures their products meet the necessary fire safety standards.
- Material Selection: The UL 94 standard classifies materials into different flame retardant ratings, such as V-0, V-1, V-2, HB, and non-rated. This classification system enables manufacturers to choose appropriate materials based on the desired level of fire resistance. It provides a clear benchmark for comparing different materials and selecting those that offer the required level of flame retardancy for PCB applications.
- Consumer Confidence: Consumers have a high level of recognition and trust in the widely acknowledged UL 94 standard. When manufacturers label their products as compliant with this standard, it instills confidence in consumers that the product has undergone rigorous testing to ensure its fire safety. This enhances the reputation of the manufacturer and builds trust among customers.
Overall, the UL 94 standard plays a crucial role in ensuring the fire safety of PCBs and other plastic materials. It provides a standardized method for evaluating flame retardancy, helps with regulatory compliance, assists in material selection, and boosts consumer confidence in the safety of products.
what is flame retardant 4?
FR4, short for Flame Retardant 4, refers to a composite material extensively employed in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It consists of two layers of fiberglass matting bonded with a resilient and anti-corrosive phenolic resin surface. The Electronic Industries Alliance has standardized the material as EIA-481.
One of the notable benefits of FR4 is its remarkable flame retardant characteristics.It is designed to be flame, heat, and smoke resistant. FR4, composed of glass woven fabric with aluminum foil on both sides, exhibits resistance to melting, burning, or charring when subjected to flames. This high resistance to flames makes it an ideal material for PCBs where fire safety is a concern.
Furthermore, FR4 has the highest flame resistance rating possible, known as a Class 1 rating. This rating indicates that FR4 meets stringent fire safety standards and exhibits exceptional resistance to flame spread.
Apart from its fire retardant characteristics, FR4 offers several other desirable properties. It is mechanically robust, providing excellent strength and durability. The material is also chemically stable, allowing it to withstand various environmental conditions and resist degradation over time. Furthermore, FR4 is known for its affordability, which contributes to its widespread adoption within the electronics sector.
Due to its versatile nature and affordability, FR4 has become synonymous with PCB technology, often referred to as “FR-4,” representing the fourth generation of Fiberglass Resin. Its widespread use is attributed to its flame resistance, mechanical strength, chemical stability, and overall reliability in electronic applications.
What's the difference of FR-4 between UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB?
UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB are classification ratings for flame retardant materials used in the electronics industry, specifically in printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other applications requiring fire safety considerations. The key difference between UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB FR-4 materials lies in their flame retardancy mechanisms. UL94 V-0 materials are formulated with advanced additives that enable them to self-extinguish quickly when exposed to a vertical flame, generating a protective char layer that prevents the spread of fire. On the other hand, UL94 HB materials do not possess the same level of fire-resistant additives, resulting in slower extinguishing times and potential dripping or particle formation during combustion. Understanding the distinctions between these two classifications is essential for selecting the appropriate material based on specific application requirements and fire safety standards.
- Flame Retardancy Mechanism:
The key distinction between UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB FR-4 materials lies in their flame retardancy mechanisms. UL94 V-0 materials are formulated with advanced additives that enable them to self-extinguish quickly when exposed to a vertical flame.These additives generate a protective char layer, effectively preventing the spread of fire. In contrast, UL94 HB materials do not possess the same level of fire-resistant additives, resulting in slower extinguishing times and potential dripping or particle formation during combustion. - Fire Safety Standards:
FR-4 materials that comply with UL94 V-0 rating adhere to the most stringent fire safety regulations. They are widely used in applications where stringent fire regulations are mandated, such as electronic devices and systems operating in critical environments. The UL94 V-0 rating provides assurance that the material will not contribute to the propagation of fire or pose significant fire hazards. UL94 HB FR-4 materials, while offering a moderate level of flame resistance, may not be suitable for applications with strict fire safety requirements. - Testing Procedures:
Both UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB materials undergo standardized testing procedures to determine their flame retardant properties. The vertical flame test is commonly employed, where a specimen is subjected to a controlled flame ignition. The material’s behavior, including the time taken to self-extinguish, the occurrence of flaming drips or particles, and the propagation of fire, is assessed during the test. UL94 V-0 materials must meet more stringent criteria compared to UL94 HB materials to achieve the higher flame retardancy rating. - Impact on Material Properties:
While both UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB FR-4 materials share similar mechanical and electrical properties, the flame retardancy additives in UL94 V-0 materials can slightly impact certain characteristics. The presence of fire-resistant additives may result in a marginal reduction in specific mechanical properties, such as tensile strength or flexural modulus, compared to UL94 HB materials. However, these differences are often negligible and do not significantly affect the overall performance of the material in most applications. - Consideration of Application Requirements:
The choice between UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB FR-4 materials depends on several factors. Applications that prioritize high fire safety standards and demand superior flame retardancy should opt for UL94 V-0 materials. These may include critical electronic systems, aerospace components, or automotive electronics where the risk of fire propagation must be minimized. UL94 HB materials, while offering a lower level of flame resistance, can find suitable use in less critical applications where the fire risk is relatively low, such as certain consumer products or non-essential electronic devices.
It is crucial to carefully evaluate the fire safety requirements and regulatory standards of the intended application when selecting between UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB FR-4 materials. This ensures that the chosen material provides adequate protection against fire hazards while considering cost considerations and performance requirements.
| Factor | UL94 V-0 | UL94 HB |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Retardancy Mechanism | Advanced additives that enable self-extinguishing and char layer formation to prevent fire spread | Lack of advanced additives, resulting in slower extinguishing times and potential dripping or particle formation |
| Fire Safety Standards | Meets highest level of fire safety standards, suitable for critical applications | Offers moderate level of flame resistance, may not be suitable for strict fire safety regulations |
| Testing Procedures | Must meet more stringent criteria to achieve higher rating | Tested using standardized vertical flame test to assess behavior |
| Impact on Material Properties | Slight reduction in specific mechanical properties compared to UL94 HB | Similar mechanical and electrical properties, but with slight differences due to fire-resistant additives |
| Consideration of Application Requirements | Optimal choice for high fire safety standards and superior flame retardancy | Suitable for less critical applications with lower fire risk |
UL94 V-0 and UL94 HB FAQ.
How is the flammability of materials tested in UL 94?
The flammability of materials is tested in UL 94 by exposing samples to a controlled flame ignition source under specific conditions. The samples are evaluated based on parameters such as burn rate, afterflame time, afterglow time, and the presence of flaming drips.
How does UL 94 testing contribute to product safety?
UL 94 testing plays a crucial role in ensuring product safety by assessing the flammability characteristics of plastic materials. The test results help manufacturers select suitable materials that comply with fire safety regulations, minimizing the risk of fire incidents and enhancing overall product safety.
Are there any additional tests related to flame resistance in addition to UL 94?
Yes, there are other tests related to flame resistance, such as the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) test and the Oxygen Index (OI) test. These tests measure the minimum concentration of oxygen required to support sustained combustion and provide additional information about the material’s flame resistance.
What are some common applications of materials tested under UL 94?
Materials tested under UL 94 find applications in various industries, including electronics, automotive, construction, aerospace, and consumer goods. They are used in products such as electrical enclosures, connectors, wiring, insulators, housing for appliances, and automotive components where fire safety is critical.
Can UL 94 test results be used for regulatory compliance?
Yes, UL 94 test results are widely accepted for regulatory compliance purposes. They help manufacturers demonstrate that their products meet fire safety standards set by organizations like Underwriters Laboratories (UL), the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), and government authorities.
Should any constraints be taken into account when carrying out UL 94 testing?
While UL 94 testing provides valuable information about material flammability, it is important to note that the test conditions do not always represent real-world scenarios. Therefore, it is essential to consider other factors and conduct additional tests specific to the intended application to ensure complete fire safety evaluation.
What does "FR4 flame resistant" mean?
“FR4 flame resistant” refers to the characteristic of FR4 material, which is extensively used in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs), to resist or slow down the spread of flames when exposed to heat or fire. It is an important property that ensures safety and helps prevent fires in electronic devices.
Where are UL94 V0 materials commonly used?
UL94-V0 materials are commonly used in applications where fire safety is critical. They find extensive use in electrical and electronic equipment, automotive components, and other products that require a high level of flame resistance.
Why is it necessary to use materials that comply with the UL94 standard to manufacture UL94 PCBs?
Using materials that comply with the UL94 standard to manufacture UL94 PCBs ensures that they have excellent fire resistance. In electronic products, especially those involved in high temperatures, high voltages, or flammable environments, good fire resistance is crucial. Materials used in UL94 PCBs have undergone rigorous testing and can self-extinguish or reduce the spread of flames, thus reducing the risk of fire and protecting the safety of equipment and personnel.
How do vertical specimens of plastic materials differ from other testing configurations?
Vertical specimens of plastic materials, as specified in ISO 9772, are oriented in a vertical position during testing. This configuration is chosen to simulate a scenario where the material is mounted vertically, such as in wall coverings or panels. By evaluating the burning behavior of plastic materials in this specific orientation, ISO 9772 aims to assess their performance in situations where vertical flammability is a concern.
How can a product obtain UL certificates?
To obtain UL certificates, a product must undergo comprehensive testing and evaluation by UL laboratories. The specific requirements for certification depend on the type of product and the applicable safety standards. The product’s design, construction, materials, and performance are assessed against predefined criteria. If the product meets all the necessary requirements, UL issues a certificate indicating compliance with the relevant standards.
What is the role of Underwriters Laboratories (UL) in relation to ISO 9772?
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is an independent safety science company that conducts testing, certification, and validation of products, including plastic materials. While ISO 9772 is an international standard, UL laboratories often perform testing and evaluation based on this standard to assess the flammability characteristics of plastic materials. UL’s expertise and reputation contribute to the credibility and acceptance of test results obtained according to ISO 9772.
In summary, flammability ul94 hb FR-4 materials offer a moderate level of flame resistance and can be suitable for applications with lower fire safety requirements. While they may not meet the stringent standards of UL94 V-0 materials, UL94 HB materials still provide a certain degree of fire protection. At JHDPCB, we have extensive expertise in working with UL94 V0 FR-4 materials and ensuring their proper utilization in electronic manufacturing. Our team is equipped with the knowledge and experience to assist customers in selecting the most appropriate material for their specific application requirements, taking into account factors such as cost, performance, and fire safety considerations. With our dedication to quality and compliance, customers can trust in our ability to deliver reliable and safe solutions using UL94 V0 FR-4 materials.