About JHDPCB
We are delivering industry-leading PCBs on time at competitive costs.
Founded in 2009, JHDPCB has more than 15 years of experience manufacturing full range of PCBs. It is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the R&D, production and sales of printed circuit boards (PCBs). The company sells HDI boards, multi-layer boards, rigid-flex boards, heavy copper boards, metal substrates, high-frequency boards, flexible boards, etc. The sales area covers Europe, America, Southeast Asia and other countries and regions.
Our goal is to be China’s TOP5 PCB manufacturer.We are committed to providing high-quality, industry-leading PCBs on time at competitive costs.You can rely on us to get the most cost-effective PCB by our expertise and large-scale production.
We provide customers with high-quality PCBs with rich experience and first-class precision equipment, not limited to any type of PCB. Just contact us and send your Gerber file and request for material and quantity and we will give a price shortly.
We also offer a free PCB file check to help you get the correct PCB design before full production and avoid costly mistakes. All our designers are compliant with the ISO9001:2015 quality management system and our in-house quality control department will verify that your prototype meets our and your high standards before we send it to you.
We also provide one-stop service from PCB fabrication to PCB assembly. Whether you want PCB or PCBA, it can be produced in our own factory. We have our own full set of world-renowned PCB production lines and surface treatment lines, reflow soldering and SMT machines, etc. Can better control quality and provide you with faster delivery, we will take our advantages and ingenuity to help all customers solve their PCB needs.
The company is committed to technological innovation; continuous expansion of the product application field, constantly upgrades our industry structure by following instant market change, and actively targeting at the high-end PCB market. After years of development, JHDPCB has accumulated plentiful industry experience, advanced technology and efficient management team of innovation, JHDPCB also establish a modern operating management system, including R&D, sales and service section. Our products are widely used in network communications, automotive electronics, security, consumer electronics, LED display and AI, biometrics, IOT, intelligent wear, UAV and so on.
*Data as of August 2023
Top 4 Reasons Why You Should Buy PCB From Us
Reliable Quality
Reliable quality has always been the core of our service. Therefore,we continue to invest in the latest technology and facilities, including some of the most advanced PCB production and testing equipment.
Our achievements are recognized through customer success and recognition, industry recognition and continuous quality improvement.
JHDPCB has passed a series of PCB industry certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IPC Class 2/3, UL, RoHS and REACH to ensure the safety and quality of PCB products.
Lower Cost
Since 2009, JHDPCB has continuously promoted the improvement of production efficiency and the reduction of costs. We are committed to providing customers with the most economical PCB. We produce high-quality PCBs with the low price through large-scale production, extremely high production efficiency and less labor costs. By cooperating with us, you can reduce procurement costs by at least 30%
Lower The Cost


Quick Delivery
Our 12-hour quick response sales team, full-link digital order management system, sufficient raw material inventory, strong company strength and stable cooperative logistics partners, every step is for your fast delivery.
Professional Team
Since JHDPCB was established, it has accumulated rich experience in PCB production. At present, we have a R&D team of 150+ people and a first-line production team of 4,000+ people, providing high-quality PCB products to customers in more than 120 countries around the world. Our employees are our greatest treasure.
JHDPCB has a mature production system. One-stop PCB manufacturing factory that supports all demanding high-demand design and manufacturing. Including Fr4, Aluminum Substrate, FPC, HDI, Laser Drilling, Micro Via, Heavy Copper Circuit Board and High Frequency Board. A complete and efficient production line guarantees that we can deliver more than 10,000 square meters of printed circuit boards per month. JHD will offer you unbeatable deals and high quality PCBs.
We also provide turnkey PCB assembly services for small to medium to high volume production. We are able to carry out the entire process including: ordering all components, PCB fabrication to assembly, testing and final shipment. We have the ability to help you develop new ideas to the ground.
Application Case

led
One of the roles that PCB plays in LED applications is to dissipate heat from the bulb. High temperature will reduce the average life of the LED. Therefore, PCBs used for LEDs are usually made of aluminum, which can transfer heat better than other metals. This eliminates the need for an additional heat sink in the design, which means it can be made more compact.
In the evolving landscape of online gaming, casinos with no account have emerged as a convenient and streamlined option for players in Australia. These innovative platforms eliminate the traditional registration process, allowing players to enjoy their favorite games without the hassle of lengthy sign-up procedures. By simply making a deposit through trusted payment methods, Australians can dive right into the action, enjoying instant play across a variety of slots, table games, and live dealer experiences.
The concept behind no account casinos is to provide a user-friendly, efficient, and secure gaming experience. They offer privacy and quick transactions, often with the ability to play immediately and withdraw winnings without delay. These casinos utilize cutting-edge technology to verify players' identities through their banking details, maintaining security and compliance with gambling regulations.
As the trend of no account casinos continues to gain popularity in Australia, players are appreciating the ease and speed with which they can jump into the fun, making these casinos a go-to choice for those seeking straightforward, high-quality online gambling.
Villento Casino Canada boasts a reputation for delivering an elegant and immersive online gaming experience. With a library comprising hundreds of games, including progressive jackpots, classic slots, table games, and video poker, the Villento Cad casino caters to diverse gaming preferences. Their games are powered by Microgaming, a leading software provider known for high-quality graphics and smooth gameplay.
Security is paramount at Villento Casino, where players can rest assured their personal and financial information is meticulously protected with advanced encryption technologies. The casino's fair play practices are underpinned by its eCOGRA certification, ensuring a transparent and trustworthy gaming environment.
The sign-up process is straightforward, incentivizing new players with generous bonuses spread over initial deposits. In addition, the 24/7 customer support and a rewarding loyalty program further align with the casino's commitment to user satisfaction. For Canadian players seeking a refined and reliable online casino experience, Villento Casino stands out as a premier choice.
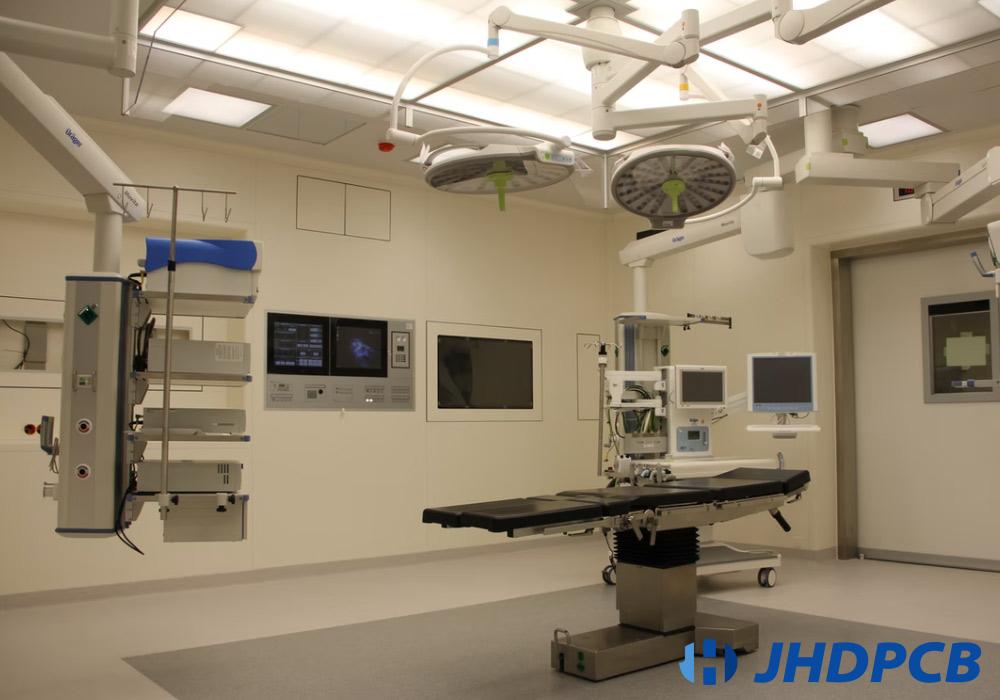

medical instruments
PCBs play a role in equipment used for diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, etc. The healthcare industry is using more and more PCBs to improve various functions. Special care must be taken to ensure reliability when producing medical PCBs, because proper functions are essential to the health of patients. Therefore, many medical PCBs are high-density interconnects or HDIs.

Consumer Electronics
Smart phones, computers and many other consumer products that people use every day require small PCBs with a large number of connections to function. With the application of various electronic products with advanced functions to life, PCB has become an important part of our daily life.






