LED Module – Efficiency, Longevity, and Design Flexibility
Light Emitting Diode (LED) modules have revolutionized the way we think about lighting technology. They offer a range of advantages over traditional lighting technologies, including high energy efficiency, long lifespan, low maintenance and led module replacement costs, and flexibility in design and application.
LED modules, in particular, offer a simple and effective way to implement LED lighting in various settings. In this blog post, we will delve into the different types of LED modules, their advantages, and how they are manufactured to ensure top-end quality and durability.
Join us as we explore the world of LED modules and gain a deeper understanding of their many advantages for modern lighting needs.
What is an LED Module?
A light-emitting diode or LED module is an advanced solid-state lighting technology that uses light-emitting diodes as a source of illumination rather than electrical filaments or gas. LEDs are semiconductor devices that produce visible light when an electric current passes through them.
LED modules contain multiple LEDs in a single fixture. The LEDs are mounted on a circuit board that provides electrical connections and mechanical support. Also, they require a driver or power supply to operate and often include additional components like lenses, heat sinks, and reflectors.

LED modules offer several benefits over incandescent or fluorescent lighting. They are more energy efficient, durable, and environmentally friendly. LEDs are solid-state, so they are resistant to damage from vibration and have an exceptionally long useful life. Also, they do not contain hazardous materials like mercury which requires special disposal.
The principle behind the LED is the electroluminescence effect—the emission of light due to the flow of electrons in a semiconductor material. When an LED is switched on, electrons move across the semiconductor material and fall into holes. This releases energy in the form of photons, resulting in light emission. The color of the light depends on the band gap of the semiconductor. Materials like gallium nitride can emit blue and UV light, while indium gallium nitride produces colors from blue to deep red.
The principle behind the LED is the electroluminescence effect—the emission of light due to the flow of electrons in a semiconductor material. When an LED is switched on, electrons move across the semiconductor material and fall into holes. This releases energy in the form of photons, resulting in light emission. The color of the light depends on the band gap of the semiconductor. Materials like gallium nitride can emit blue and UV light, while indium gallium nitride produces colors from blue to deep red.
Many LED modules, known as RGB LED modules, contain multiple LEDs in red, green, and blue colors which can be combined to produce a wide color gamut. These LED modules are commonly used for dynamic digital signage, mood lighting, and entertainment lighting applications where variable and vibrant colors are desired. Overall, LED technology has revolutionized the lighting industry with its energy efficiency, durability, and optimal light quality.
What Types of LED Module Lights Are There?
LED module lights are versatile and energy-efficient lighting solutions that are widely used in various applications such as signage, backlighting, architectural lighting, and general illumination. They are available in a variety of colors, correlated color temperatures (CCT), shapes, sizes, efficiencies, luminous flux, lamp bead package types, and power options (AC/DC). In this section, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the different types of LED module lights.
1.Color
LED module lights are available in a diverse range of colors, including:
Monochromatic LEDs:
These LEDs emit a single color, such as red, green, blue, amber, or white. They are commonly used in signage, decorative lighting, and other applications where a specific color is required.

RGB LEDs:
RGB (red, green, blue) LEDs can produce a wide spectrum of colors by combining the primary colors at different intensities. They are used in applications like architectural lighting and stage lighting, where dynamic color control is desired.

Tunable White LEDs:
These LEDs can emit a range of white light from warm white to cool white by adjusting the intensity of two or more LED chips. Also, these white LED strobe modules are used in applications that require adjustable color temperatures, such as human-centric lighting and circadian rhythm lighting.

2.Correlated Color Temperature (CCT)
LED module lights are versatile and energy-efficient lighting solutions that are widely used in various applications such as signage, backlighting, architectural lighting, and general illumination. They are available in a variety of colors, correlated color temperatures (CCT), shapes, sizes, efficiencies, luminous flux, lamp bead package types, and power options (AC/DC). In this section, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the different types of LED module lights.
LED module lights are available in various correlated color temperatures, which are measured in Kelvin (K). Common CCT ranges include:
Warm White (2700K – 3000K): This range provides a cozy, inviting ambiance and is used in residential and hospitality applications.
Neutral White (3500K – 4100K): This range offers balanced, natural light that is suitable for office spaces, retail stores, and other commercial applications.
Cool White (5000K – 6500K): This range emits a crisp, bright light that is ideal for task lighting, outdoor lighting, and industrial applications.
3.Shape and Size
1. Classification Based on Shape
Linear LED Modules: These modules have a rectangular shape and are used in applications like under-cabinet lighting, cove lighting, and linear architectural lighting.
Round LED Modules: These modules feature a circular shape and are commonly used in downlights, spotlights, and other applications that require focused light.
Flexible LED Modules: These modules consist of flexible LED strips that can be bent and shaped to fit curved surfaces and intricate designs. They are used in applications like signage, decorative lighting, and curved architectural lighting.
2.Classification Based on Size
LED modules come in various sizes to suit different applications and installation spaces. They can be broadly classified into small, standard, and large-size categories based on their dimensions and power ratings.
Small LED Modules:
Compact or small LED modules typically measure less than 50mm x 50mm. They are ideal for confined areas with limited space, such as led display module units, signboards, decorations, etc. These modules are very versatile, energy-efficient, and safe to use without issues like overheating or flickering.
Standard LED Modules:
Standard LED modules are medium-sized, usually 50mm x 50mm to 100mm x 100mm. They are well-suited for both indoor and outdoor use and often come with additional features like integrated heat sinks, waterproof housings, and mounting tapes. These modules are more robust and help minimize color shifts or light degradation over time.
Large LED Modules:
Large LED modules are bigger in size, typically larger than 100mm x 100mm. They provide a bigger offset between the emitting surface and LED chips, usually over 50mm, allowing for better visibility and a wider beam angle. The larger size also means higher power ratings and greater energy efficiency. These modules are ideal for applications where a strong, evenly distributed light output is required over a bigger area.
4.Module Efficiency
LED module efficiency refers to the amount of light produced per unit of electrical power consumed. It is measured in lumens per watt (lm/W). High-efficiency LED modules are preferred in applications that require significant energy savings, such as street lighting and industrial lighting. There are the following types according to module efficiency.
High-efficiency LED: These modules produce more than 120 lumens per watt. They feature the latest chip technology to maximize light output and minimize heat and power loss. These modules are ideal for applications requiring maximum light output with lower power consumption.
Standard LED modules: They have an efficiency of 80 to 120 lumens per watt. They offer a good balance of light output, cost, and performance for many general applications.
Low-efficiency LED modules: These modules produce less than 80 lumens per watt. They tend to be older or lower-cost options and are not as energy efficient.
5.Luminous Flux
Luminous flux, measured in lumens (lm), indicates the total amount of visible light emitted by an LED module. The required luminous flux depends on the application and desired light output.
Low-lumen LED modules produce less than 500 lumens. They are suitable for task lighting, accent lighting, and indicator lighting.
Medium-lumen LED modules produce between 500 and 1000 lumens. They are useful for general-purpose lighting in medium-sized areas.
High-lumen LED modules produce more than 1000 lumens. They are required for bright area lighting, floodlighting, or high-bay commercial and industrial applications.
6.Lamp Bead Package Type
LED module lights use different lamp bead package types, which affect their performance, size, and reliability. Some common package types include:
SMD (Surface Mounted Device): SMD packages are compact and versatile, making them suitable for a wide variety of applications. Like bottom solar LED modules, they are commonly used in LED modules for indoor and outdoor lighting.
COB (Chip-on-Board): COB packages consist of multiple LED chips mounted directly onto a substrate, resulting in high light output and improved thermal performance. They are typically used in high-power LED modules for applications like street lighting and high-bay lighting.
MCOB (Multiple Chips-on-Board): MCOB packages feature multiple COB packages on a single substrate, offering enhanced light uniformity and optical control. They are used in high-quality LED modules for applications like downlights and spotlights.
7.AC/DC Power Options
LED module lights can operate on either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) power sources. AC modules usually have an integrated driver that converts AC power to DC, simplifying installation and reducing system complexity. DC modules require an external driver to convert AC power to the appropriate DC voltage. DC-powered led flasher modules are often preferred in applications that require centralized power management or dimming control.
Overall, LED module lights offer a wide array of options in terms of color, CCT, shape, size, efficiency, luminous flux, lamp bead package type, and power options. Understanding these various types will help you select the most suitable LED module light for your specific application.
The Manufacturing Process of PCB LED Module
JHDPCB is a leading provider of printed circuit board (PCB) solutions, specializing in the manufacturing of high-quality PCB LED modules. With years of experience and advanced equipment, At JHDPCB,we have the capability to produce high-quality LED modules lights tailored to clients’ needs. Here, we want you to have a look at the manufacturing process of PCB LED modules at JHDPCB.

1.Bare Board Manufacturing
The first step in the PCB LED module manufacturing process is the production of bare boards. JHDPCB uses state-of-the-art equipment and materials to create the foundation for your LED modules.
Material Selection:
JHDPCB offers a variety of materials to suit your specific LED module requirements. Some of the common materials used in LED PCBs are:
- Aluminum PCBs – Aluminum base PCBs are the most popular for LED modules due to their excellent heat dissipation properties, high thermal conductivity, ease of processing, and low cost compared to other options. Aluminum can quickly and efficiently spread the heat generated by LED chips to avoid overheating. The technology to mount and package LED chips onto aluminum PCBs is well-developed, making it a straightforward process for manufacturers with a low risk of issues or defects. Although aluminum is inexpensive compared to other metals, it has suitably high performance for most LED applications.
- Copper PCBs – Copper base PCBs have even better thermal performance than aluminum and are a higher-end option for very high-power LED modules that produce more heat, especially in enclosed or poorly ventilated fixtures. However, copper is more difficult and expensive to process compared to aluminum. Copper PCBs are less commonly used due to significantly higher cost, except for niche applications where maximum heat dissipation is the top priority.
FR4 PCBs – FR4 PCBs are rarely used in LED modules due to their poor thermal conductivity, which prevents effective heat dissipation from the LED chips. FR4 can only be used for very low-power LED modules in well-ventilated fixtures. Otherwise, the heat buildup would quickly damage the LEDs. FR4 is primarily used when its low cost is the most significant factor and high thermal performance is not required。
Design and Layout
JHDPCB’s experienced team of engineers will work closely with clients to develop a custom design and layout for the PCB. Factors considered include:
- Power requirements and heat dissipation needs
- Spacing and layout of components for optimal light output
- Dimensions and form factor
- Interconnects, solder pads, and wiring patterns
- Test points and other special requirements
This collaborative design process ensures that the board meets your specific requirements and performance needs.
2. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Once the bare boards are ready, the next step is the SMT process, where JHDPCB’s advanced equipment and skilled technicians ensure the accurate placement of components onto the PCB.
Solder Paste Application
Solder paste is applied to the PCB using a stencil, ensuring that the right amount of paste is applied to the correct locations. The solder paste will temporarily hold components in place before soldering.
Component Placement
JHDPCB’s high-speed automated pick-and-place machines accurately place the LED components, resistors, capacitors, and other surface mount devices onto the PCB according to the design. The assembled PCBs are then passed through a reflow oven, where the solder paste melts and form a strong, reliable connection between the components and the board under controlled heat and cooling cycles.
3. Soldering
After SMT, any through-hole components like LEDs, connectors or switches are soldered onto the PCB using either wave soldering or selective soldering, depending on the design and requirements. Wave soldering can solder all through-hole components simultaneously while selective soldering is for specific joints.
4.Testing
We at JHDPCB are committed to delivering high-quality, reliable LED modules. As such, all PCB LED modules undergo rigorous testing to ensure proper functionality and performance.
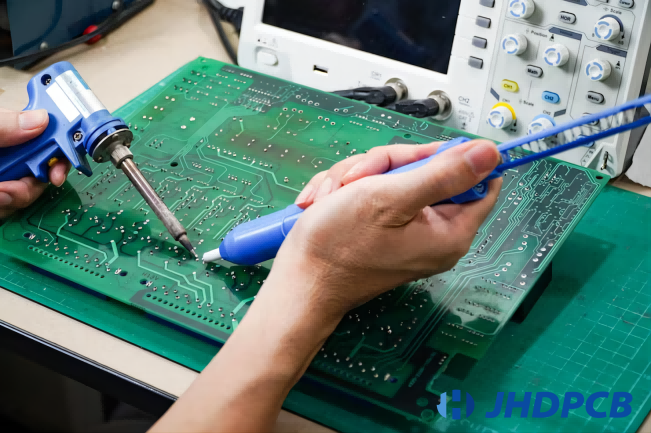

Method#1: Visual Inspection
Experienced technicians perform a visual inspection of each module to identify any potential defects or issues with the soldering, components, or PCB.
Method#2: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
JHDPCB uses advanced AOI equipment to inspect the solder joints and verify the placement and orientation of components on the board. AOI can detect issues that may be missed during visual inspection.
Method#3: Functional Testing
Finally, each PCB LED module is tested for functionality, ensuring that it meets the performance requirements outlined by the client. This may include tests for operating current, voltage, light output, color temperature, etc.
By combining skilled technicians, advanced equipment, and a commitment to customer satisfaction, we try to consistently deliver high-quality PCB LED modules tailored to clients’ needs. With years of experience manufacturing LED-based PCB assemblies, JHDPCB has the capabilities and expertise to produce LED modules for a wide range of applications.
Applications of LED Modules
LED light modules have been widely used for various applications beyond brightening up outdoor advertisements and shop signage. They are ideal for:
1. Outdoor Landscape and Accent Lighting:
LED module lights can be used to highlight the architectural details of your house or light up pathways and driveways. Their low voltage (as a 12v led module) and energy efficiency make them suitable for outdoor use.
2.Interior Lighting:
LED strip lights and modules are great for indirect lighting in cupboards, cabinets, and tight spaces where bulky lights cannot fit. They provide decorative accent lighting for bathrooms, bedrooms, and living rooms. Their small size and low profile allow them to be hidden neatly along edges and corners.
3.Vehicle Lighting:
LED modules are commonly used to light up the dashboard, interior, license plate, and headlights of vehicles. They are durable and long-lasting, unaffected by vibrations
4. Task Lighting:
LED modules are ideal as night lights, reading lights, and table lamps where focused bright light is needed. They produce little heat compared to incandescent bulbs.
5.Flashlights and headlamps:
LED module lights are used in place of incandescent bulbs in flashlights and headlamps as they have a longer lifespan and lower power consumption.
6. Led Modules for Signs
LED modules are a common choice for electric signs due to their high brightness, long life span, and energy efficiency. LED sign modules typically use high-powered SMD or Through-hole LEDs arranged in patterns to form words, icons, or shapes. Signage LED modules allow you to create vivid, visually striking displays that attract attention. They provide consistent, flicker-free illumination with very little brightness degradation over time.
Overall, LED module lights are highly flexible and configurable. They can be cut, connected in series, and reworked to achieve a customized illumination effect for any application. Their low-profile design and availability in multiple colors open up many possibilities for creative lighting installations.
At JHDPCB we specialize in high-quality and high-power LED lighting solutions for both indoor and outdoor uses. Our products range from spotlights, floodlights, downlights, and streetlights to tunnel lights. LEDs with different color temperatures and CRI ratings are available to suit any lighting requirement. Add LED lights to brighten up your offices, parking lots, retail stores, hospitals, and more.
Advantages of LED Modules
LED modules offer a wide range of advantages over traditional lighting technologies, making them a popular choice for a variety of applications. Here are some of the key advantages of LED modules:
Energy Efficiency:
LED modules are highly energy efficient and consume significantly less power compared to traditional lighting technologies. They convert most of the energy consumed into light, producing little heat, which means less wasted energy and lower electricity bills. Also, LED channel letters are more energy efficient and durable than channel letters that use neon or fluorescent tube lighting. They require minimal maintenance.
Long Lifespan:
LED modules have a much longer lifespan than traditional lighting technologies, which means lower maintenance and replacement costs. LED modules can last up to 50,000 hours or more, depending on the quality of the module and the application.
Low Maintenance and Replacement Costs:
LED modules require minimal maintenance, as they do not have any moving parts that can wear out. This means lower servicing costs and less downtime for the application. Additionally, due to their long lifespan, LED modules do not need to be replaced as frequently, leading to further cost savings over time.
Flexibility in Design and Application:
LED modules are highly versatile and can be designed in a variety of shapes and sizes to suit different applications. They can also be used in a range of applications, including indoor and outdoor lighting, automotive lighting, backlighting for displays and signage, horticulture lighting, and more.
How to Choose an LED Module?
When choosing LED modules, there are several factors that should be taken into consideration to ensure the best performance for the intended application. Here are some of the key factors that should be considered:
Power
The wattage and lumens of the LED module will determine the brightness and energy consumption of the module. It is important to choose a module with the appropriate power for the intended application, taking into account factors such as the size of the space, the desired level of brightness, and the energy efficiency requirements.
LED modules typically range from 1W to 100W or more. Higher power means a brighter light but also produces more heat which needs to be managed. Consider how much light is needed for your application and the power required. For example, a 5W LED module may be bright enough for a small cabinet light but not a spotlight.
Voltage
The most common voltages are 12V and 24V DC. Ensure your power source matches the LED voltage. If it does not, you will need a driver to convert the voltage. Higher voltage LEDs, like 24V, allow for lower current so they lose less power through the wiring. But 24V drivers and power supplies are more expensive.
Number of LEDs
Most modules have 30 to 60 LEDs or more. More LEDs mean a higher maximum power and lumen output. It also allows for a wider beam angle – 60 LEDs could be 120 degrees while 30 LEDs might be 60 degrees. More LEDs cost a bit more but allow for a brighter, wider light.
Dimensions
LED modules range from 1-4 inches up to large panels 2×4 ft. Consider where the module will be mounted and the dimensions of your fixture or housing. Leave room for airflow and heat sinking on higher-wattage modules. Strip modules are good for task lighting, spots for spotlights, and panels for area lighting.
IP rating
IP ratings range from IP20 to IP68. An IP20 module has no protection, while IP68 can be submerged 2 meters deep. Choose an IP based on your environment – outdoors requires at least IP65, while damp/wet areas should be at least IP44. Higher IPs may require special mounting and heat-conductive but electrical non-conductive materials.
Cost:
Higher wattage, more LEDs, special features like color changing/dimming, and higher IP ratings mean higher costs. Basic 12V strip modules start around $5 while high-power IP68 modules can be $50-$100 or more. Consider your budget and keep features simple if cost is a concern.
Application:
Consider how and where the LED module will be used to determine which features are most important. For example, an outdoor spotlight would need high power, a wide beam, and a high IP rating while an indoor task light can have lower power and IP rating.
Heat management:
Higher-power LED modules generate more heat, so consider how the heat will be dissipated in your design. You may need a fixture with built-in heat sinks or fans.
Color Temperature and Color Rendering Index (CRI):
The color temperature and CRI of the LED module will determine the quality of the light produced. Color temperature refers to the perceived warmth or coolness of the light, while CRI measures how accurately the colors of objects appear under the light source. It is important to choose LED modules with the appropriate color temperature and CRI for the intended application, taking into account factors such as the mood or atmosphere desired and the color accuracy required for the application.
Beam Angle and Optics:
The beam angle and optics of the LED module will determine the direction and spread of the light produced. It is important to choose LED modules with the appropriate beam angle and optics for the intended application, taking into account factors such as the size and shape of the space, the desired level of brightness, and the direction of the light required.
Dimming and Control Options:
The dimming and control options of the LED module will determine the flexibility and ease of use of the module. It is important to choose LED modules with the appropriate dimming and control options for the intended application, taking into account factors such as the desired level of control and the ease of use required.
Choose JHD to Provide You With Customized High-Quality LED PCB Modules
We highly recommend JHDPCB as your supplier for customized high-performance LED PCB modules. We have significant expertise in developing LED modules that deliver exceptional results and meet the precise needs of our clients.
JHDPCB LED modules are designed for high heat dissipation and high lumen output, ensuring an optimal balance of performance and energy efficiency. We offer full control over correlated color temperature (CCT) and provide modules in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and specifications tailored to your product.
We use only the highest quality components to achieve maximum light output, superior heat management, and long operational life. Our LEDs contain no toxic heavy metals and are fully RoHS compliant, reflecting our commitment to environmental sustainability.
With JHDPCB as your partner, you gain access to the latest LED technologies, customization options, and manufacturing capabilities. We support you through every step of the process with our dedicated team of engineers and client support staff. Experience, innovation, and quality are the hallmarks of JHD’s LED modules.
Please contact us today to discuss how we can develop a customized solution for your lighting needs. We are confident that you will be fully satisfied with the results and delighted with the partnership. We look forward to working with you on your next project to make it a shining success.
Frequently Asked Questions About LED Modules
Is it possible to receive free samples of LED module lights?
Yes, typically we can provide free samples for you to assess the quality of our products. We also offer the ability to mix and match different LED module series.
What is the typical delivery time for LED light modules?
Our top-selling series is PCB LED module lights, and we can typically provide samples within 3 days. For larger orders, we can typically deliver 50000pcs within 15 days or 300000pcs within 30 days. However, delivery times may vary depending on factors such as inventory availability and shipping distance.
Do you offer ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) services for LED modules?
Yes, we have a strong R&D team that has successfully developed over 30 types of LED modules for ODM projects. We can work with you to create customized LED module designs that meet your specific requirements. Please feel free to discuss your needs with us to see how we can help.
What are LED display modules?
LED display modules contain arrays of individual LEDs arranged in pixels, 7-segment patterns or other configurations to display alphanumeric characters, icons, or shapes. They are used in digital signs, industrial indicators, and similar applications.
What material is an LED module?
LED modules are made with a printed circuit board substrate as the base. Electronic components like surface mount devices, resistors, and capacitors are soldered to the PCB. The LEDs themselves are small semiconductor chips made of materials like gallium arsenide, indium phosphide, and silicon carbide.
What voltage is the LED module?
Most low-power LED modules operate at voltages between 3 and 24 volts DC. Higher-wattage LED arrays and strips require higher input voltages of up to 120V. Voltage matching is important to prevent damaging the LEDs.
How many volts is 1 LED?
A single LED typically requires between 1.8 and 3.6 volts to illuminate, depending on factors like color and material. Red LEDs require less voltage while blue and white LEDs require more. The specific forward voltage is listed in the LED datasheet.