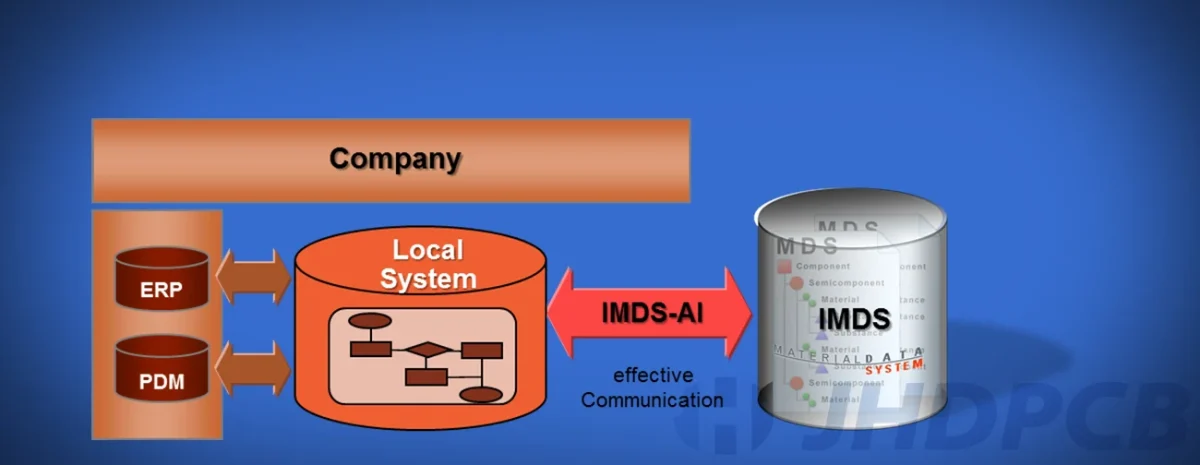
(IMDS) International Material Data System Guide.
In today’s interconnected world, the demand for safe and environmentally friendly products is higher than ever before. The International Material Data System (IMDS) has emerged as a powerful tool in achieving these goals by enabling transparency and traceability of materials used in the manufacturing process. At JHDPCB, a trusted and professional PCB manufacturer, we recognize the importance of IMDS in ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and promoting sustainability.
In this article, we aim to demystify IMDS and shed light on its significance in the PCB manufacturing industry. We will explore how IMDS facilitates the disclosure and management of material data, ensuring compliance with regulations such as RoHS and REACH. By delving into the intricacies of IMDS, we will showcase JHDPCB’s commitment to environmentally conscious manufacturing practices and our dedication to providing our clients with compliant and sustainable PCB solutions.
Join us on an enlightening journey through the realm of IMDS, as we unravel its role in promoting environmental responsibility and trust in the PCB manufacturing process.
What does IMDS stand for?
The automobile industry manages information about the materials and compounds used in vehicles using the (IMDS) International Materials Data System, an online Material Information Database database. Ford, Opel, Porsche, Volkswagen, Volvo, Daimler, DXC, and Audi all contributed to its development. In order to specify the materials for which Material Data Sheets (MDS) are prepared, the IMDS Steering Committee has released a number of recommendations. Each recommendation includes MDS guidelines for several material classes. How to disclose declarable compounds found in components and materials is explained in the IMDS recommendations. IMDS, which was created in 2000 to comply with environmental laws including the EU’s Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive and the End-of-Life Vehicles Directive, has expanded to include at least 62 international automobile OEMs. As more manufacturers joined the community at the same time, MDS grew to become a universal standard that is adopted by practically all worldwide OEMs. National and international standards, regulatory requirements, and commitments to automakers and their suppliers can all be met with the help of lMD.
IMDS Recommendation 019 is one of them and it pertains to electrical and electronic components. On October 30, 2003, it was originally authorized and made public. The new Rec 019 procedure was created in 2013 to satisfy the REACH communication requirements as well as the expanded requirements of the End of Life Motor Vehicles Directive (2000/53/EC). Rec 019 details the development of hybrid electronics suitable for automotive applications, printed circuit boards (PCB/PWB), materials at all supply chain levels, electrical/electronic components, and flexible circuit boards (FCP). Instead of reporting a fully disaggregated BOM, REC 019 offers suppliers a modular way to reporting materials in electronic components, including leaded components. The IMDS Steering Committee has created a number of standard modules to streamline the material data reporting procedure. It lays out the procedure providers must follow to make sure the data they submit completely complies with the legal requirements in the IMDS database, in addition to involving the compilation of standardized data sheets.
Benefits of applying IMDS for automotive manufacturing.
The automobile industry created the web-based IMDS Support application to manage and distribute data regarding the material make-up of vehicles and their parts. Manufacturers use it to gather and manage this data in a consistent way while suppliers use it to offer information about the materials used in their goods. The IMDS system offers a centralized database of data on materials used in the production of vehicles and is a crucial tool for ensuring compliance with international laws like the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directives of the European Union.
Using the IMDS system to accomplish compliance and sustainability in the automobile manufacturing Industry has a number of advantages:
- Environmental Compliance: IMDS services make sure that automotive goods and the parts that make them up abide by environmental laws like RoHS, which forbids the use of hazardous materials in electronics. The manufacturing sector may avoid exorbitant fines and penalties and safeguard the environment by tracking the materials used in production and assuring compliance.
- Transparency of Materials: The IMDS system makes the materials used in Automotive Manufacturing Material Data and their parts transparent. To demonstrate compliance with environmental rules and company sustainability goals, this information can be shared with clients, authorities, and other stakeholders. The identification of possible areas for improvement by suppliers can also spur the development of new sustainable materials.
- Risk reduction: The IMDS system lowers the possibility of non-compliance with environmental laws by giving suppliers and manufacturers access to and updating common Auto Parts database of material data. As a result, there is less chance that compliance will be violated as a result of inaccurate or outdated data, and everyone is guaranteed to get the most recent information.
- Data security: IMDS does not reveal the names of lower-level suppliers and permits the designation of non-GADSL chemicals as confidential or the use of wildcards and wild symbols.
- Cost reduction: Lack of communication between automakers and suppliers increases supply chain risk and compliance difficulties, which raises costs (unnecessarily). In addition to ensuring data lifetime through constant regulatory adjustments and supplier involvement, IMDS also contributes to cost savings by discovering safer, more environmentally friendly substitute materials that may be used in the manufacturing process to better comply with global laws.
- Enhancing Sustainability: The automotive sector as a whole may enhance sustainability by choosing safer, more environmentally friendly materials. Committing to enhancing environmental health can enhance a variety of factors, including the standing of automakers and suppliers, sales figures, consumer loyalty, and more.
Advantages of using IMDS to provide data to customers:
- It can be used by both first- and second-tier suppliers in the automotive industry, as well as all manufacturers of vehicles and parts.
- To supply part information to numerous manufacturers, suppliers just need to use one IMDS system.
- Supplier expenses are decreased by utilizing a single central system.
- The IMDS data structure can be added to the built-in database to enhance its capabilities.
- IMDS can ensure Ford’s Substance Management Standard (RSMS) and assist in meeting national and European inspection criteria, such as the European End-of-Life Vehicle Directive (2000/53/EC).
IMDS allowable material percentage variance range.
To begin assembling components in IMDS, ask your supplier for a material declaration. This appears to be section 3 of an SDS or a spectrometer analysis. The most fundamental substances in existence will be listed. Additionally, each substance’s CAS (Chemical Abstracts Service) number needs to be listed. The statement will list all metals other than iron.
Verify that the sum of all percentages is 90–100%. Only 10% of the overall material composition can be classified as miscellaneous or “not declared” in IMDS (which can be used to protect confidential information). Please be aware that only specific percentage variations are permitted under IMDS Recommendation 001 when utilizing percentage ranges rather than exact percentages in material declarations:
- A discrepancy of three percentage points is allowed for ranges of 0% to 7.5%. (For instance, if the range starts at 0%, it can only rise by 3%.)
- A five percentage point variation is allowed for ranges of 7.5% to 20%.
- A discrepancy of up to 10% is permitted for percentage ranges of 20% to 100%.
The average of the two percentages inside the range is utilized if your range falls outside of the one above. In order to determine the allowed range and not receive the Recommendation 001 warning, Consider your material classification carefully.
To identify the right table, utilize the material categorization.
Be aware of your lowest limits.
When deciding which row in the table to select, pay close attention to breakpoints. If on a border, the table’s higher row is used.
Find the corresponding M value.
The maximum permissible upper bound value that would not cause warnings is obtained by adding M to the lower bound.
Please be aware that while though the IMDS system enables you to issue MDSs with warnings, it is ultimately up to your client to decide whether to do so.
How Does IMDS work?
Before and during the component approval process, IMDS assists OEMs and large-tier suppliers in verifying the contents of their bought parts. Before PPAP approval can be given to the supplier, the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) requires IMDS submission for each part number.
The Material Data Systems for the automotive industry are accessible to anyone with a computer and an internet connection. Companies must register on the website in order to use this system, after which they are given a special identification number that is used to log their data under a firm ID. When suppliers send a material data sheet (MDS) to a client, a permanent connection is made between the two parties, and by the time the vehicle is completed, the IMDS ought to be an accurate representation of the supply chain flow.
The Bill of Materials should be grouped in order to identify each subcomponent. Next, state the material(s) that each is made of, describing the makeup of the material further by naming the constituent parts. Each component is weighed and measured, and the database record is arranged according to the product structure key.
The multinational Material Data System contains a developing catalog of every component used in every car made by a participating multinational automaker. Even if it is not required by law, developing a habit of carefully documenting data will help your supply chain and get your business ready for potential regulatory changes.
Material classification of International Material Data System?
| Classification | Definition | Example / Designation |
|---|---|---|
| 0 Undefined | This classification cannot be used. | / |
| 1 Steel and iron materials | This classification cannot be used. | / |
| 1.1 Steels / cast steel / sintered stee | This classification should be used only when classifications 1.1.1 and 1.1.2 are not appropriate, for example for sintered steel. Sintered materials with both metal oxides and metals do not fit in this classification, for example ceramic magnets. | Sint-D01 P1011Z |
| 1.1.1 Unalloyed, low alloyed | A content of at least 95% iron is expected. Generally, the content is above 98%. | DC 01 SPCC |
| 1.1.2 Highly alloyed | There are two definitions for highly alloyed steels. In IMDS, the second definition is generally understood to be the “right one” 1. If the content of at least one alloying element is above 5 % you speak of highly alloyed steel. 2. Highly alloyed steel consists of less than 95% iron and more than 5% further metallic | X30Cr13 S42000 SUS420 |
| 1.2 Cast iron | This classification cannot be used. However, legacy data can be continued to be used. | / |
| This classification cannot be used. However, legacy data can be continued to be used. | This classification cannot be used. However, legacy data can be continued to be used. | EN-GJL-100 FC100 |
| 1.2.2 Cast iron with nodular graphite / vermicular cast iron | Nodular graphite flakes are used in approximately spherical cast iron part. | EN-GJS-400-15 FCD400-15 |
How to create International Material Data System?
On the IMDS homepage, under IMDS Information Page, click Register Your Company to register your business. It is only permitted for one business or location of commercial operation to register with IMDS. To access the IMDS system, click the “IMDS Login” button on the IMDS Information page. To log in, the user can input their user ID and password.
What is the relationship between PPAP and IMDS?
Manufacturers and suppliers can discuss and approve production designs and processes before, during, and after manufacturing with the use of the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP), a standard procedure for the automotive and aerospace sectors. PPAP was developed to make it easier for manufacturers and suppliers to understand each other’s requirements. It also makes sure that the processes used to make parts can reliably create them at the required production rates during normal production runs. The PPAP Handbook was originally a publication of the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) to manage PPAP procedures for those in the automotive industry. Now it is gradually being applied in all walks of life.
All materials used in the construction of an entire vehicle are gathered, preserved, analyzed, and archived in IMDS. The requirements placed on automakers and their suppliers by local, national, and worldwide standards, rules, and regulations are assisted by IMDS.
By comparing the provided data with lists of prohibited compounds from regulatory sources (GADSL, [3] REACH, ELV, etc.) and using a computer-based system, IMDS can identify hazardous and regulated substances. As a result, OEMs are able to track down dangerous compounds to specific parts and collaborate with suppliers to mitigate, manage, or completely remove dangers.
Not just substances that should be notified and prohibited (such as Cr VI, Hg, Pb, and Cd), but all substances must be declared at 1 gram resolution or better in the Material Data Sheet (MDS) in IMDS. In order to fulfill the requirements of the ELV Directive, the OEM must have a thorough understanding of the components and materials of a product before it can be delivered to a deconstruction business.

Each supplier is required to submit information about the parts they offer to their direct clients as part of the system’s fundamental workflow concept. The customer-supplier relationship is maintained when every link in the supply chain provides data in this manner, simulating the actual supply chain part flow. A contractual need for PPAP, which is a component of the common automotive quality system, is often data entry in IMDS.
Prior to and throughout the component approval process, IMDS assists OEMs and big suppliers in confirming the substance of the parts they have sourced. Before PPAP approval is granted to the supplier, the Production component Approval Process (PPAP) requires IMDS submission for each component number. You are unable to supply parts without IMDS data.