Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Guidelines.
jhdpcb@gmail.com
The meaning of PPAP in quality is the Production Part Approval Process, which is a beneficial method to instill confidence in suppliers of components and their production techniques. In today’s competitive environment for manufacturing, it is crucial to manage costs and maintain top-level quality to ensure the success of the company. Growing markets across the globe, combined with increasing costs of materials, equipment, and workforce, have led to a rise of outsourced parts. Many component parts are being shipped to overseas manufacturers that in turn require longer waiting times and higher order volumes. Therefore, it becomes essential to deliver quality parts that meet the customer’s specifications from the beginning and always. Primarily, PPAP was used by the aerospace and automotive sectors, though several industries are now using PPAP to enhance communication and provide quality products. The primary source of information about PPAP in the automotive sector is the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) guidebook, which has been published as a standard reference for this Production Part Approval Process. The aerospace ppap standard establishes guidelines for Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) and PPAP process requirements in the aviation, space, and defense industries to guarantee completely integrated phased product development procedures.
What is PPAP quality?
The PPAP handbook is a standardized procedure widely adopted by industries to ensure that the supplier’s manufacturing process meets the engineering design and product specifications. During PPAP, suppliers and customers collaborate on the necessary requirements for approving parts produced by the supplier. The principles of PPAP are universally applicable to all types of parts and goods and help eliminate delays and non-compliances by implementing a standardized approval process.
PPAP is a critical procedure in the manufacturing industry, particularly in aerospace and automotive, to ensure that supplier-made parts are consistent. It is a detailed process, consisting of 18 steps, which ensures that each component meets expectations and is manufactured with high quality every time. Although PPAP originated in aerospace and automotive, it has gained widespread use across the manufacturing industry to facilitate important activities and promote cooperation between customers and suppliers.
Furthermore, PPAP forms an essential component of Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP), particularly in stage four, where the emphasis is on the validation of the product and process. The complete PPAP guidelines are published by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) and are available for purchase.
Implementing a Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is intended to:
- Guarantee that the supplier has the ability to meet the manufacturing and PPAP quality standards necessary for providing components to the client.
- Show proof that the supplier comprehends and satisfies the design record and specification requirements of the customer’s engineering.
- Exhibit that the implemented production process has the capability to produce the component that consistently satisfies all criteria during actual production at the quoted production rate of the manufacturing process.
The PPAP procedure is structured to prove that a supplier has created their design and production process to adhere to the customer’s requirements, minimizing the risk of failure by proficient utilization of APQP. As such, applications for approval of the component should be presented in formal PPAP format and documented outcomes are obligatory when necessary.
The demands of PPAP for PCB.
- Prototypes of printed circuit boards (PCBs)
- Flowchart of the process
- Part Submission Warrant (PSW)
- Effect Analysis (FMEA) andFailure Mode of the process
- Control Plan for the process
- Inspection of dimensions
- Use of Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Report on thickness of plating
- Report on wettability
- Certification of raw materials
While there is no direct correlation between printed circuit boards (PCBs) and production part approval procedures (PPAP), the automotive electronics sector may incorporate the PPAP process for PCBs as an essential electronic component. PPAP is a standardized procedure that establishes the certification process for a supplier’s manufacturing process to comply with product and engineering requirements. Through PPAP, customers and suppliers identify the necessary standards to obtain approval for the supplier’s assembly of components to ensure their credibility and dependability. When supplying PCB products to automotive manufacturers, suppliers are required to undergo PPAP certification to guarantee that the manufacturing process conforms to the specific standards of the manufacturer. JHD has the ability to provide a complete Production Part Approval Process.
Why should the production part approval process be performed?
PPAP holds significant importance as it guarantees that every crucial component required for an automobile or equipment is made to the precise specifications consistently. It provides distinct directives, ensuring that suppliers fully comprehend what is expected of them and thus facilitating better communication throughout the process. The PPAP car quality criterion is a crucial requirement for automotive spare part suppliers to ensure that their manufacturing processes fulfill customer specifications and requirements, guaranteeing consistent standards of quality in the parts manufactured.For manufacturers, PPAP ensures sound product quality and peace of mind that their stipulations will be fulfilled throughout the production phase. This in turn reduces the likelihood of any setbacks or corrective measures needing to be taken, resulting in a more efficient and seamless process overall.
The PPAP procedure certifies that the supplier comprehends all engineering design specifications and requisites of the customer and that the system has the ability to produce products that consistently match these requirements throughout an actual production run at the stated production rate. As PPAP and other quality techniques are increasingly incorporated in different industries, it is crucial for parts suppliers to gain insight into the prerequisites of PPAP to retain their competitiveness.
As a supplier of high-quality electronic components, JHD plays a key role in ensuring that the PPAP process runs smoothly. With its extensive knowledge and expertise in the field of electronics manufacturing, JHD can guarantee that all parts are produced to the highest standards. We have the ability to provide all necessary documentation, including Engineering Change Notices (ECNs), and have the ability to provide pre-PPAP samples for field testing. Our quality management system ensures that all materials used in production meet or exceed the customer’s specific requirements, providing the evidence required to verify the material composition of the part. Overall, JHD’s capabilities make it an indispensable partner in the PPAP process, ensuring that all parts meet the necessary standards and specifications and are delivered on time and within budget.
What particular difficulty(ies) does this tackle?
- The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) provides an understanding of the details required to gain approval for a part and establishes a standard procedure for approving parts.
- The PPAP also outlines the procedure for obtaining approval for parts/processes post modifications in design or process, ensuring all submissions are accompanied by sufficient data to maintain product consistency.
- Additionally, the PPAP documents part conformance upon launch, allowing for the evaluation of deviations from original specifications.
- In addition, it furnishes complete design documentation to ensure that the status of part design can be traced back to its origin.
- Furthermore, the PPAP regulates the process of product and process changes by providing an approval outlet for every modification. This guarantees conformity to the subsequent level assembly/process.
What are the 5 levels of PPAP?
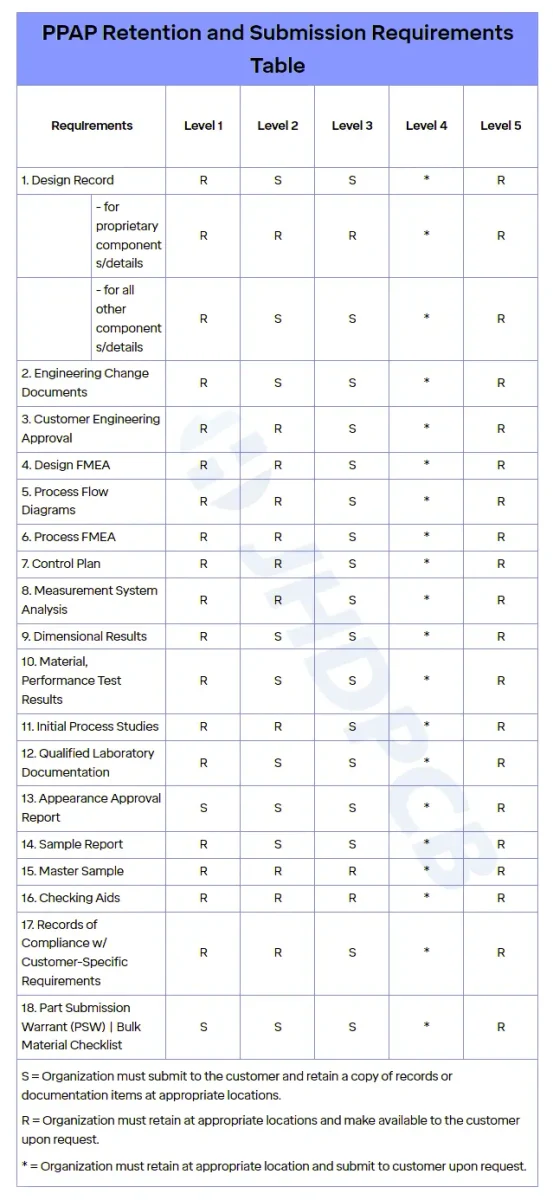
Depending on their business partners, suppliers may be required to provide PPAP elements. There are five distinct levels of PPAP submission requirements, and while manufacturers and suppliers may maintain certain documents, it is crucial to complete all of the 18 necessary PPAP elements at each specified level.
To determine whether a PPAP is necessary, it is crucial to understand the five levels of PPAP and their corresponding submission requirements. Here’s an overview of each level of PPAP and how to identify whether you need to furnish a PPAP:
Level 1 PPAP
Typically, the OEM is the sole recipient of a part submission warrant (PSW) that suppliers submit. However, if a component affects product appearance, a supplier or component manufacturer may be required to provide an appearance approval report (AAR). Additionally, in cases where the PPAP process entails the shipment of bulk materials, a bulk material requirement checklist is also necessary.
Level 2 PPAP
In the level 2 ppap, suppliers are required to provide a PSW, along with an AAR and a checklist for bulk material requirements, if applicable. Along with product samples, the supplier is also expected to submit limited supporting data, including design records for sellable products, material performance testing outcomes, dimensional results, qualified laboratory documents, and engineering change documents, along with any requests to modify parts or products.
Level 3 PPAP
In the ppap level 3, suppliers should provide all their manufacturing quality certifications from Level 2, along with seven or eight of the remaining 18 PPAP elements. These components consist of a Design Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (DFMEA), Process Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (PFMEA), process flowchart, initial process capability studies, documentation demonstrating adherence to Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) specifications, measurement system analysis (MSA) studies, and control plan. The control plan outlines any distinct features and inspection methods required for product delivery. When the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) conducts a trial run with prototypes, it is the responsibility of the supplier or manufacturer to furnish engineering approval as evidence of quality assurance in production.
Level 4 PPAP
Manufacturing quality control leaves it up to the OEM to determine most document requirements. Nonetheless, suppliers are still responsible for providing a PSW and bulk material requirements checklist if applicable. The remaining PPAP elements are left to the discretion of the OEM. However, suppliers or manufacturers are advised to prepare and keep all other PPAP documents in case the OEM requests them.
Level 5 PPAP
To ensure quality assurance during manufacturing, a PSW and product samples must be provided at Level 5 of PPAP. Additionally, all other relevant PPAP elements should be kept at the manufacturing sites and be readily available for the OEM to inspect if necessary.
How do you decide on a PPAP submission level?
| PPAP 5 Levels of Submission: | |
|---|---|
| Level | Details |
| Level 1 | Part Submission Warrant (PSW) only submitted to the customer. |
| Level 2 | PSW with product samples and limited supporting data. |
| Level 3 | PSW with product samples and complete supporting data. |
| Level 4 | PSW and other requirements as defined by the customer. |
| Level 5 | PSW with product samples and complete supporting data available for review at the supplier’s manufacturing location. |
What elements does the PPAP quality document contain?
Presented here is a comprehensive list of all 18 PPAP elements, each with a brief description for clarity:
Design Documentation
The design documentation submitted for PPAP must contain copies of both the customer’s drawings and the supplier’s own drawings, along with a copy of the purchase order. If deemed necessary, the supplier may also be required to provide documentation regarding the composition of the materials used.
- To ensure accuracy in both the ordering of the part and its revision level, the purchase order is used for confirmation purposes.
- The design engineer carries the responsibility of verifying that both sets of drawings match and that all critical and key characteristics have been identified.
- Documentation detailing the composition of the materials used is necessary to provide evidence that the parts are manufactured according to the specific requirements of the customer.
Engineering Change Documentation
When a PPAP is necessary due to a modification request for a part or product, the PPAP package must include the documentation that outlines and approves the change. Usually, this paperwork includes a replica of the Engineering Change Notice (ECN), which mandates validation from the engineering department of the customer.
Customer Engineering Approval
If included as a component of the PPAP, the supplier is obligated to provide proof of endorsement from the engineering department of the customer.
- In cases where the customer deems it necessary, they may request pre-PPAP samples for onsite testing purposes. These samples must be generated as true-to-production parts and must be shipped with a waiver in order to permit the testing process. Once the testing has been finalized, an approval form will be provided by the test engineers and submitted as a part of the PPAP documentation package.
- When submitting parts to a customer for approval prior to attaining PPAP approval, it is generally required to supply a copy of the “Temporary Deviation” document.
Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
DFMEA is a multifunctional assessment of design risk that scrutinizes the potential failure modes, their effects on the product or customer, and the likelihood of their occurrence.
These failure modes may comprise:
- Product defects
- Safety and compliance concerns
- Diminished functionality or lifespan of the product
The DFMEA is a dynamic record that requires regularppap review and revision during the entire lifespan of the product.
Process Flow Diagram
In a visual representation, the Process Flow Diagram illustrates the complete assembly procedure for either the final product or an individual component. This diagram entails the material reception, assembly process, testing and inspection, reparation, and eventual delivery of the product.
Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
PFMEA is an evaluation of every step in the manufacturing process to detect any potential quality risks and record implemented corrective actions. This record remains a dynamic document, even after the product achieves stable production, and necessitates frequent updates.
Control Plan
The Control Plan is a result of the PFMEA process, which compiles a comprehensive list of all special product features and inspection techniques required to deliver quality products consistently meeting customer expectations.
Measurement System Analysis Studies
MSA research analyzes the measurement equipment implemented during assembly or QC inspections, including conducting GR&R tests. It is mandatory to integrate maintenance records for all gauges and measuring equipment, and the performance of the measurement system should be monitored over time.
Dimensional Results
To authenticate that the product satisfies the print criteria, it’s necessary to carry out a dimensional inspection of sample parts. Random pieces from a significant production batch, usually no less than 30 units, are selected for examination. Each specification on the engineering drawing is measured during final assembly to ensure compliance. The corresponding data is entered into a spreadsheet, which forms part of the PPAP submission.
Records of Material / Performance Tests
- Included in this section should be a duplicate of the Design Verification Plan and Report (DVP&R), which provides a comprehensive summary of all part validation tests. The report should detail every test performed, including an explanation of the testing methodology and results.
- This section may additionally comprise of duplicates of all certification documentation for every listed material (such as steel, plastics, and more) featured on the blueprint. The certification records must demonstrate conformity with the precise specifications detailed on the print.
Initial Process Studies
Every production process will undergo preliminary process research that includes the application of Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts focused on critical product traits. These studies confirm that critical procedures are stable, exhibit normal fluctuation, and operate in close proximity to the target nominal value.
Qualified Laboratory Documentation
The qualified laboratory records include industry certifications obtained by any laboratory that participated in executing validation testing. This pertains to either an internal testing lab or any external contracted facilities engaged in conducting validation or material certification testing.
Appearance Approval Report
The Appearance Approval Inspection (AAI) is relevant for parts that impact only the visual presentation. This report confirms that the customer has inspected the finished product and ascertains compliance with all design-specified appearance criteria. Appearance prerequisites could contain details on color, texture, and other similar features.
Sample Production Parts
Following the conclusion of product development, sample production components are sent to the customer for approval and usually consigned to either the supplier’s or customer’s storage facilities. The PPAP documentation generally comprises an image of the production components in addition to details regarding their designated storage location.
Master Sample
The master sample refers to the last product sample that is examined and approved by the customer. Operators are trained using this master sample and it is utilized as a standard benchmark for comparison in cases where quality questions regarding production parts may arise.
Checking Aids
- This comprehensive inventory itemizes inspection aids utilized in the production process. The list must encompass all instruments employed to measure, test or examine parts during assembly. It must feature a description of the tool and also specify its calibration schedule. Checking aids may include models, templates, attribute gages, contour, variable gages, and check fixtures.
- According to customer requirements, MSA is required for all inspection aids.
Customer Specific Requirements
The submission package includes a section dedicated to outlining any exceptional customer requirements. When dealing with bulk materials, it is important to record any customer-specific requirements on the “Bulk Material Requirements Checklist.”
Part Submission Warrant
The Part Submission Warrant (PSW) provides a summary of the entire PPAP submission. The customer necessitates a PSW for every part number unless stated otherwise. The PSW comprises the following components:
- The cause for submission (e.g. alterations in design, yearly re-evaluation, etc.)
- The scope of documentation conveyed to the customer
- Confirmation of part compliance with customer conditions
- A designated section provided for any essential clarification or remarks
- Endorsement by an authorized supplier representative, including their contact information
- A space for the customer to indicate their decision concerning the submitted PPAP.
The process of PPAP is a comprehensive and time-consuming procedure. The package encompasses documentation of various cross-functional tools and confirms the supplier’s ability to fulfill all customer requirements. By providing customers with sufficient information, PPAP allows for thorough scrutiny of all aspects of design and production procedures in order to ascertain that only top-quality products are approved for shipment to end customers.
How to perform PPAP in quality?
The procedure starts with the supplier delivering a sample part to the customer, who examines and authorizes it or demands modifications. Following the approval of the component, the supplier ships a production quantity to the customer, who re-evaluates and decides whether or not to accept it.
PPAP in quality control is carried out in three phases: planning, production and post-production.
- During the planning phase, the supplier and customer collaborate to establish a PPAP submission that contains a detailed part description, manufacturing process specifications, and quality control strategies.
- During the production phase, the supplier manufactures the components based on the customer’s requirements and provides them to the customer for approval.
- During the post-production phase, the customer affirms that the parts were fabricated properly and grants permission for their shipment.
3 basic principles for establishing PPAP.
Similar to other procedure-centered actions, there are some essential factors that need to be taken into account in order to guarantee on-time and error-free delivery. Let’s examine three of these basic principles:
- It is crucial to ensure that the correct resources are allocated. Don’t assume that a few extra workers in manufacturing will be able to carry out the ppap quality process effectively. To achieve a high-quality PPAP submission, it is essential to have not just sufficient personnel, but individuals with appropriate experience and training.
- Effective planning is crucial for successful delivery. Since PPAP is a component of Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP), it is unsurprising that planning plays a critical role in ensuring a successful PPAP submission. To succeed, it is vital to allocate sufficient time, resources, and skilled personnel dedicated to delivering high-quality output and not leave it to chance.
- Include all of the essential components. It may seem like a simple task, but with 18 elements to contemplate and provide proof for, it can be effortless to overlook one element. It is critical to assign individuals with specific accountabilities for delivery and to organize internal evaluations and inspections as you establish your PPAP data in order to ensure that all critical components are covered.
When is the production part approval process performed?
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is generally required for new parts or products, as well as for changes to existing products or processes:
- A newly introduced component or item.
- Alterations/corrections to products: design, materials, supply, and functionality.
- Modifications/corrections to the process: approach, tools, site, and inspection standards.
- Tooling that has been inactive for over a year.
Based on the guidelines set forth in the PPAP manual, the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is usually carried out before production commences or when significant changes are made to the production process or parts. The goal of the PPAP is for suppliers and customers to come to an agreement regarding the prerequisites required for the approval of supplier-manufactured parts. The PPAP production report evaluates 18 factors, including design, and verifies the manufacturing procedure by inspecting components before, during, and after production runs.
To sum up, PPAP is executed in accordance with industry standards and protocols, prior to the start of production or following significant changes to the production process or parts, in order to demonstrate that the engineering design and product specifications have been met by the supplier’s manufacturing process.
What benefits does PPAP provide for the entire manufacturing process?
Emphasizing the benefits of PPAP is essential to comprehend the significance of this process, given that it has aided in achieving customer contentment across various enterprises. Some of the benefits worth mentioning include:
- A uniform process for part approval
- Assurance that the parts comply with customer requirements
- Proof of process stability
- Management of changes made to products and processes, offering an approval method for all modifications to guarantee compliance with subsequent assembly/stages
- Prominent improvement in quality compared to previous batches as it links customer demands and grievances with assembly.
- It is a clear affirmation of the commitment to lessen production costs in enterprises. With PPAP, businesses can optimize manufacturing assembly and increase profitability.
- Facilitates precise identification of problems in any industry.
- Decreases manufacturing times, which is among customers’ primary demands.
As is evident, the advantages center around the customer and the enterprise, aiming to provide superior products while streamlining the entire production process, resulting in more economical and expeditious procedures.
APQP vs PPAP.
What is APQP?

Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) is a specified methodology utilized to introduce a new product into the market or implement modifications to an existing product. A Cross-Functional Team (CFT) consisting of engineering, manufacturing, quality control, procurement, and distribution experts conduct APQP to ensure conformity with customers’ specifications.
PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) is a fundamental component of APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning).
5 Phases of APQP.
- Program Planning and Definition.
- Verification of Product Design and Development.
- Verification of Process Design and Development.
- Validation of Product and Process, Production Feedback.
- Implementation, Evaluation, and Remedial Action
The fourth stage of the APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) process integrates the PPAP (Production Part Approval Process).
How PPAP affects APQP?
When PPAP outcomes do not fulfill customers’ expectations, it often indicates a malfunction in the APQP process. The production trial operation is the examination for both APQP and PPAP. If flawed components are found in the final trial product, manufacturers must investigate the supply chain to locate where APQP or PPAP has failed.
JHDPCB is a fast and reliable PCB supplier. We are very good at implementing PPAP management processes to ensure the quality and reliability of parts and products produced in the automotive electronics industry. We have advanced production equipment and technology, and strictly follow the quality management principles and standards in the production process. At the same time, we are able to respond to customer inquiries in a timely manner and provide efficient services, including fast shipment, competitive market prices and high-quality PCBs.