Ultimate Guide to PCB Prepregs: VS core VS laminate.
jhdpcb@gmail.com
What is prepreg in PCB?
Pre-preg refers to composite fibers that have already been impregnated with a matrix material, typically epoxy.
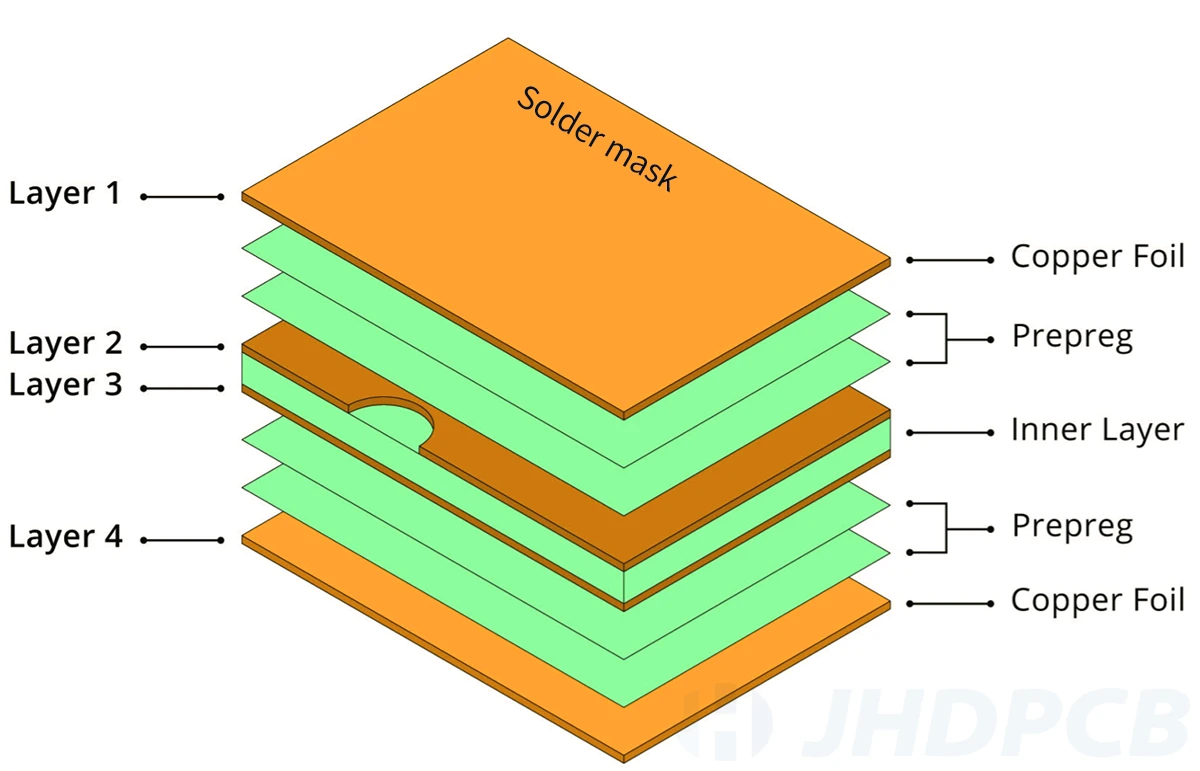
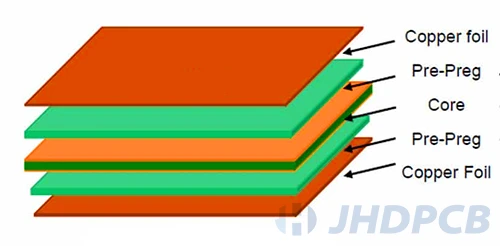
Pcb core prepreg is utilized as a dielectric material for providing insulation between a copper and a Core or between two Cores in a PCB. Prereg is simply an insulation layer. Since it can integrate copper foil with the core, it can be called a binding material.
Users can also modify Prereg as a special dielectric material as desired. By combining specific catalysts and additives, they can convert specific portions of Prepreg into conductive regions.
Prepreg is FRP-reinforced material pre-impregnated with resin. In the majority of situations, the resin is epoxy, in addition to thermosetting resin and thermoplastic resin. Even though both are technically prepregs, there is a big difference between thermosetting and thermoplastic prepregs.
Characteristics of prepregs.
Advantages of Prepregs
- Prepreg expel excess resin during curing, it will not result in excessive hand paste, large amounts of resin, and messy roller as the greatest strength characteristics.
In manual laying, it is tedious to achieve a resin content of 50%. That is, the finished laminate weighs 50% fabric and the rest is 50% resin. A typical hand laminate, even in vacuum bags, ends up with a lot of excess resin. An excess resin will increase the brittleness and decrease overall performance. In addition, most prepregs have a resin content of 35%. This is ideal for maximum curing performance and is not usually achieved in normal laminating. - Prepreg has both uniformity and repeatability.
Without the defects of lamination technology, there would be no drying points and resin-rich areas. Since the thickness of the components will be uniform, each part that comes out of the mold is likely to be the same. Even though there is still a margin of error in a vacuum, bagging technique, handling, etc., prepreg handles them well. - Prepreg is environmentally friendly and easy to handle.
Although the PCB prepreg will s, and dripping water. In addition, if the prepreg is treated at room temperature, it does not take much effort to prevent the resin from solidifying before it is ready. - Prepreg saves curing time.
The typical manual lamination is waiting for 48 hours to fully cure. But it can be used after the heat curing cycle. - Prepreg is a better cosmetic.
Manual lamination requires mold preparation and demoulding, which will directly affect the appearance of parts. However, the prepreg eliminates bubbles and produces a smooth and shiny surface.
Disadvantages of Prepregs
- Cost.
Prepreg is expensive. Even if the cost of resin, curing agent, and fabric is added up, it is not as high as the cost of prepreg. - Quality guarantee period.
Although fiberglass prepreg has a storage time of up to 6 months at room temperature 75°F. However, heat curing prepreg and high-temperature environment will affect the expiration date. Keeping the temperature of the material low is beneficial to storage because freezing will significantly prolong its life. - Necessary heat cure.
Have at least one heat source and vacuum bag. The temperature should be at least 270 degrees Fahrenheit and stay there for more than four hours. Many advanced manufacturers choose to use autoclaves, but any heat source will work.
How is the pregreg made?
Let’s have a rough look at the process of making prepreg.
- Step 1: The prepreg is made of thermoplastic or thermosetting resin. The initial stage of the production of pre-impregnated materials is very important, which directly affects the quality of the development of composite materials for specific purposes. By analyzing the application of the final composite material, we can understand the fiber and resin that can provide better performance. Reinforced prepregs are available in thermoplastics or thermosetting resins.
- Step 2: Remove excess resin from the prepreg reinforcement material. One of the advantages of taking the place of inefficient materials with prepregs is the ability to cut down the amount of waste produced during manufacturing.
Precise control of fiber-to-resin ratio and layer thickness is required during resin impregnation. After the fabric is injected with resin, the excess material on the structure is wiped off. In the meanwhile, the reinforcement proceeds to partial curing, which is called Stage B. - Step 3: Prepreg is cured at low and high temperatures. An added benefit of developing prepreg-reinforced materials is that these structures do not take as much curing time. With the start of stage B of the process, the prepreg requires refrigeration in order to cure. After a short period of refrigeration, heat and pressure are applied with a heating tool, such as an autoclave, to activate the curing process. Thermosetting and thermoplastic prepregs form durable, lightweight composite structures for a wide range of applications.
Application in the PCB Manufacturing Process
The most common application of prepreg in PCB manufacturing is to bond the copper field of copper-coated laminate to the copper foil in a multi-layer rigid PCB. Furthermore, it finds application in the production of flexible circuit or rigid-flex circuit board.
In flexible circuits with stiffened plates, PCB layers are realized from one side to multiple layers. In this case, the application of prepreg is to glue the FPC to the stiffened plate.
In stiff-flex plate types, PCB layers are double-sided to multilayer types. This construction is achieved by combining CCL with copper foil using prepregs or FPC with stiffeners.
The Differences Between PCB Core and Prepreg.
Because of the similarity between prepregs and core materials, it is easy to confuse them. In short, the core is prepreg and laminate the product. Therefore, its rigidity is much greater than prepreg. The core wire is made of fiberglass epoxy laminate with copper on both sides to make it flame retardant.
On the other hand, in the absence of lamination, the prepreg will be partially dry and less rigid than the core. Core and prepreg in PCB dielectric constant are different. The dielectric constant of the core remains unchanged, while that of the prepreg changes after laminating. Different dielectric constants are also functions of:
- Type of resin;
- Glass weave;
- Resin content;
Accurate impedance matching is difficult to achieve. In addition, the exact dielectric constant and the loss in interconnection are also difficult to predict. This is because the prepreg embryo and the core are not necessarily compatible, and the core/prepreg billet stacks have different dielectric constants.
In fact, the desired thickness can be achieved by combining the prepreg layer, where the sheets are placed on top of one another.
At high voltage, whether using PCB core or prepreg materials, there will be leakage and leakage current problems. The creep electrical specification for FR4 materials requires the electromigration of copper and growth of conducting filaments. For the sake of resolving this problem, and also to enhance the glass transition and decomposition temperature, people began to choose non-dicyandiamide resin.
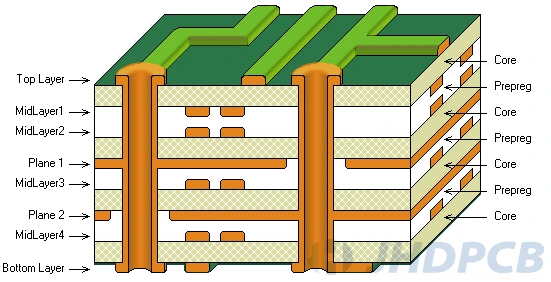
Core material and prepreg are an integral part of PCB. Although the prepreg core is the basic PCB material, the multilayer PCB is connected by prepreg. There is a clear difference between the two( prepreg vs core), the core is cured while the prepreg is plastic, meaning it can easily form flakes. The material melts at high temperatures, helping the layers fuse together. Click to view more detailed PCB core material copper clad laminate knowledge.
What is the difference between prepreg and laminate?
| Prepreg vs Laminate | ||
|---|---|---|
| Versus | Prepreg | Laminate |
| Definition | Partially or uncured core material | Fully cured core material |
| Usage | To glue two copper layers together or to combine a copper layer with a core, but to prevent the bonding of the two materials being bonded. | The copper layers are separated by a dielectric material with copper. |
| Stackup location | Between two cores or a core and copper foil. | Between copper layers or planes. May form the core of the board stackup. |
How to Choose Prepreg in PCB manufacturing?
To select the best pre preg materials, the first step is to understand the various parts of the PCB stack and their functions. The following factors need to be considered:
- Fiber genre: Glass, basalt, carbon and aramid.
- Fiber form: unidirectional or woven.
- Resin genre: Common type is epoxy. There are other resins that have had a big impact on how prepregs are used.
- Fibre aerial weight.
- Proportion of resin present: Prepreg is available according to resin thickness and standard. It can be classified as standard, medium or high resin according to resin content. How much resin content determines the pricing rate, resin content and the price is proportional.
- The effect of resin content on the properties of prepreg also includes permittivity, thermal expansivity, and accuracy of drilling and etching.
- Curing method: The curing method determines the strength and quality of the prepregs. This factor ultimately affects its application.
There are dissimilar genres of prepreg because pcb prepreg thickness and other requirements are different. We categorize Prepregs as normal resin, middling resin as well as high resin on the basis of content. Rising resin quantities translate to an elevated price point. The following is the prepreg style table commonly used by JHD, I hope it can help you understand.
| Prepreg Style | Resin Content | Glass | O/A | Delta | Unsupported Resin Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 106 | 75% | 0.0014 | 0.0023 | 0.0009 | – |
| 1080 | 65% | 0.0025 | 0.003 | 0.0005 | Very Low |
| 2113 | 56% | 0.0029 | 0.0039 | 0.001 | – |
| 2116 | 57% | 0.0038 | 0.0051 | 0.0013 | – |
| 2116 | 62% | 0.0038 | 0.0061 | 0.0023 | Very High |
| 1652 | 50% | 0.0045 | 0.0057 | 0.0012 | – |
| 7628 | 42% | 0.0065 | 0.0069 | 0.0004 | Very Low |
| 7628 | 50% | 0.0065 | 0.0085 | 0.002 | Very High |
What is resin flow in prepreg?
Resin flow refers to the melting (liquefaction) and flow of resin when the prepreg is heated under pressure. The generation of flow velocity can be affected by the rate at which pressure and resin heating takes place. The basic principle of lamination is that the resin remains fluid enough for a certain period of time to flow freely, after which the resin will solidify. The actual flow rate of the resin is of great importance to the laminating operation. Conversely, laminating conditions also affect the flow rate of the resin.
The actual flow rate will affect the properties of interlayer bonding, bonding with oxide inner copper foil, laminate bonding with ED copper foil and so on. It also impacts the whole effect of the prepreg as a bonding plate.
How to measure resin content of prepreg material?
Resin content (%) is the percentage of resin to the integral effect of prepreg. The burn-off method is the standard technique used to measure the resin content in fiberglass-reinforced prepreg and laminates. This method involves subtracting the final weight after combustion at 1100℃ from the initial weight.
The discrepancy expressed as a percentage is the rein content. Increasing or decreasing the weight of the substrate fabric, consistent coater operation, and alterings in the rheology of different batches of resin solutions can all affect the ability to control resin content.
The concrete steps of resin content testing are as follows:
- Take the prepreg sample and measure the original weight.
- Next, the sample is dipped in LR sulfuric acid (H2SO4) for a few seconds to dissolve all the resin in the acid.
- Rinse the specimen with water and let dry.
- Finally, determine the weight of the test piece. A difference in weight gives a quantitative sample of the resin content.
Resin (%)= sample weight loss/sample initial weight x100
The thickness of the laminate when pressed rest upon the resin content. Content also has a significant effect on pcb prepreg dielectric constant and other properties.
Prepreg is a kind of insulating material. As such, it is vital and plays an important role in making excellent PCBs. Prepreg is essential for any PCB manufacture.
JHD is fully aware of this point, so it strictly examines the purchase of prepreg raw materials. To ensure that every order of the customer can meet its design application. If you don’t know how to choose a prepreg, welcome to send us your production information. Our team of professional engineers will give the best suggestion according to your board design.